
Introduction
Project scheduling is an integral part of effective project management. Project scheduling includes the development of a project timeline, including tasks, resources, and milestones, that is necessary to ensure a project’s successful completion. A solid schedule can provide a roadmap for project execution, allowing project managers to allocate resources, monitor progress and recognise potential issues in advance.
In the modern workplace, having an edge in project scheduling is vital to the successful delivery of projects within the time and budget constraints. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of project scheduling. We will discuss key concepts, techniques, and best practices for project scheduling. In addition, we will analyse the challenges commonly faced in project scheduling and review tools and software solutions that can simplify and optimise the process.
Understanding project scheduling
What is a project schedule?
A project schedule is a detailed document that outlines the timeline of tasks and milestones that must be completed to accomplish the project. It acts as a roadmap for project execution and monitoring.
Components of a project schedule
- Tasks and activities
- Duration and deadlines
- Resource allocation
- Dependencies and constraints
- Milestones and deliverables.
Difference between project schedule and project plan
A project plan is a more comprehensive document that encompasses the schedule, as well as other project aspects such as scope, budget, and resources. The project schedule, on the other hand, focuses on the time aspect, including task sequencing and deadlines.
Benefits of using a project schedule
- Provides clarity and direction: A project schedule offers a clear path for project execution, ensuring that all team members are aware of their responsibilities and deadlines.
- Improves time management: A schedule helps to prioritise tasks and allocate time efficiently, reducing the risk of missing deadlines.
- Allows efficient resource allocation: A project schedule enables the optimal distribution of personnel, equipment, and materials across project tasks.
- Helps in effective risk management: A project schedule helps to identify potential bottlenecks, and resource conflicts in advance, allowing for timely risk mitigation.
By utilising these advantages, project managers can significantly improve the chances of project success and timely delivery.
Six steps to create a project schedule
A project schedule is a comprehensive document that outlines a project’s timeline. It is one of the most important project management tools. Scheduling is one of the key tasks in project management. To help you along, here are six steps that will allow you to create a solid schedule for your project.
1. Define tasks and milestones
List all the tasks that are necessary to complete the project. Then determine the project milestones, and group tasks that make up each milestone into work packages. The process of preparing a comprehensive list of project tasks is known as Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
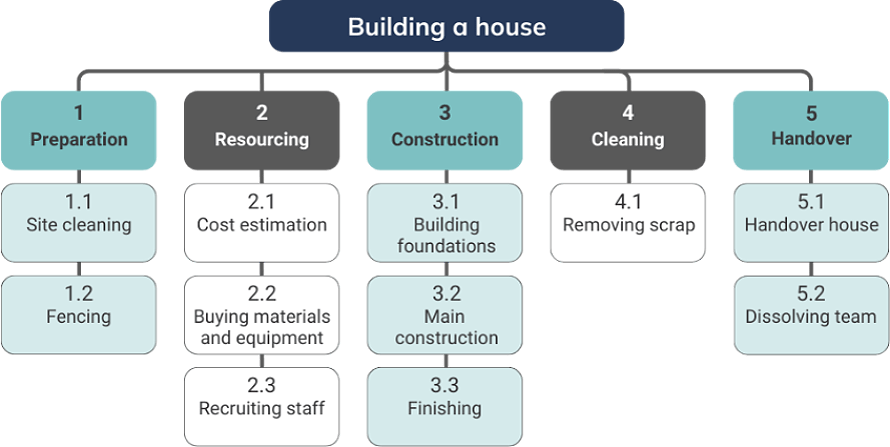
- List all required tasks
- Determine project milestones
- Group related tasks into work packages.
2. Sequence activities
Sequence the tasks, establishing the order in which the work will be performed. Use a network diagram to visualise the dependencies and the critical path.

3. Estimate task durations
Estimate the time required for each task, then assign the estimates to each task. For more accurate results, ask your team members to help, and make use of the historical data for tasks of a similar nature to the ones in the current project. As a rule of thumb, provide three-point estimates:
- Optimistic estimate
- Most likely estimate
- Pessimistic estimate.
4. Assign resources
Identify the resources needed for each task, then assign them to the relevant tasks. Be sure to consider team members’ skills and experience, availability and current workloads.
5. Finalise the schedule
Confirm the draft schedule with the stakeholders and finalise it. Be sure that the schedule is realistic and it meets the project’s objectives and constraints and use the scheduling software to create a Gantt chart (or another visual representation).
6. Share and monitor progress
Share the finalised schedule with the team members and stakeholders and track and report on the progress. Consider using project management software for real-time updates and collaboration.
- Set up regular progress meetings
- Encourage team members to report the task completions as soon as they are done
- Update the schedule if necessary to account for the actual progress.
With these steps, you can create a comprehensive project schedule that will guide your team to successful project completion.
Project scheduling techniques
There are several techniques available for the effective creation and management of project schedules. Some of these techniques include Gantt charts, task lists, and calendars. This knowledge train will cover the definition and purpose of each of these techniques, the advantages and limitations of using each, when it is appropriate to use each, and benefits for smaller projects. The knowledge train aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of project scheduling techniques to help project managers make informed decisions about which techniques to use for their projects.
Gantt charts
Definition and purpose
A Gantt chart is a type of bar chart that is commonly used in project management to visually represent a project schedule. It shows the start and end dates of project tasks, as well as their duration, as horizontal bars along a timeline. Gantt charts can also be used to display the dependencies between tasks.
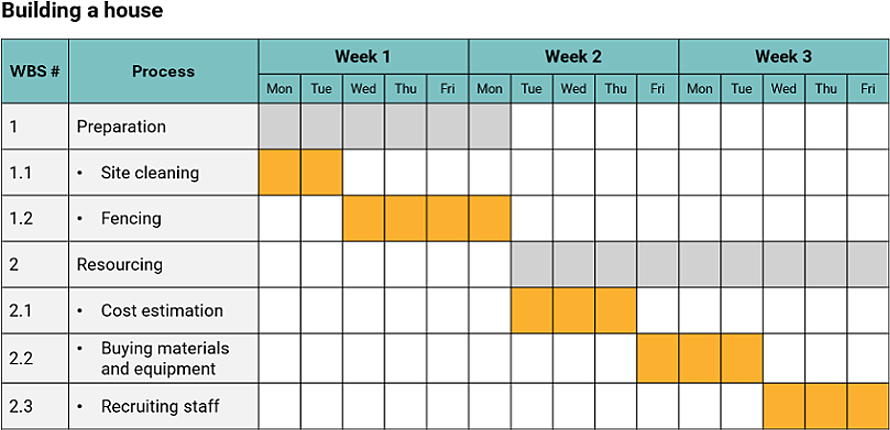
Advantages and limitations
Advantages
- Provides a visual representation of task dependencies
- Simplifies the identification of the critical path
- Capable of showing progress against the planned schedule.
Limitations
- Can become cluttered and difficult to read for larger projects with many tasks
- Can be time-consuming to create and maintain
- Limited ability to show detailed task dependencies and resource allocation.
Task lists
When to use task lists
Task lists are often used in project management as a basic tool for organising and tracking project activities. They can be useful in the early stages of a project, or as a supplement to more advanced scheduling techniques. Task lists are appropriate to use when the project is relatively simple, and the team members are familiar with the tasks.
Benefits for small projects
- Simple to develop and maintain
- Facilitate clear communication of responsibilities
- Allow quick changes and revisions.
Calendars
Uses in project scheduling
Calendars are often used in project management to help visualise and plan the timeline of a project. They can be used to track important project dates, such as milestones, deadlines, and deliverables. Calendars can also be used to provide an overall view of the project’s timeline.
Limitations of calendar-based scheduling
- Inadequate representation of task dependencies
- May lack necessary detail for more intricate projects
- Challenges in depicting tasks with varying durations.
Project scheduling techniques are an essential aspect of project management and choosing the right technique can greatly impact the success of a project. By understanding the advantages and limitations of each technique, as well as when and where to use them, project managers can effectively create and manage project schedules. Combining multiple techniques, such as using a Gantt chart to track progress and a calendar to visualise the timeline, can also be a useful strategy for managing project schedules.
Advanced scheduling concepts
The more complex the project, the more benefit can be gained from advanced scheduling techniques. CPM and CCPM are methods to take your project planning to the next level.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
Definition and importance
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique used to identify the longest path of dependent tasks in a project schedule. The critical path determines the minimum project duration.
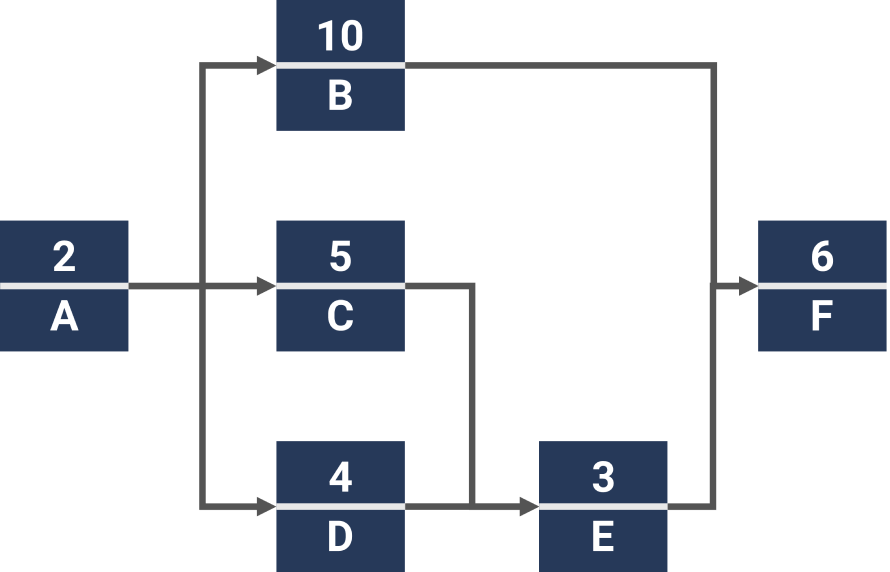
Identifying the critical path
To identify the critical path, follow these steps:
- List all tasks and their dependencies
- Estimate the duration of each task
- Calculate the earliest start and finish times for each task
- Determine the latest start and finish times without delaying the project
- Identify tasks with zero float (slack time).
Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)
Resource-based approach
Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) is a method that focuses on resource-based scheduling. It considers both task dependencies and resource constraints to optimise project schedules.
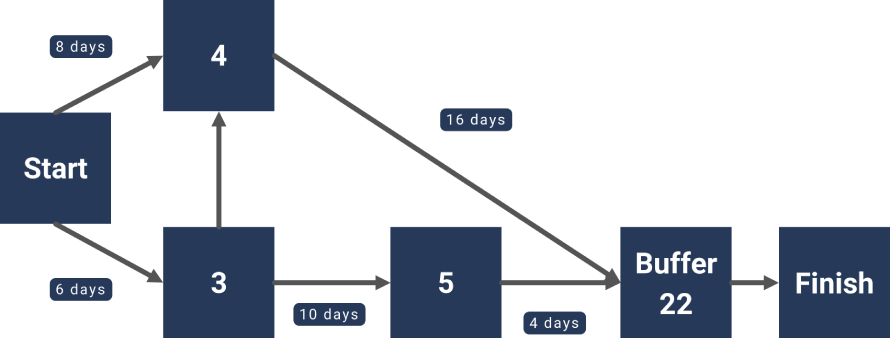
Differences from Critical Path Method
- CCPM considers resource constraints, while CPM focuses solely on task dependencies
- CCPM uses buffer time at the project level, rather than padding individual tasks
- CCPM aims to reduce multitasking and encourage early task completion.
Both methods can provide useful insights for optimising project schedules and enhancing overall project management efficiency.
Tools for project scheduling
If you’re going to be doing project scheduling on a regular basis, you might find it useful to consider using specialist software to help you with this. A quick search online will pull up a range of tools. Some popular options include:
Project management software options
- Jira: Agile project management software with customisable workflows and reporting.
- Microsoft Project: Software for creating detailed project schedules and resource management.
- Other popular options: Trello, Asana, Basecamp, etc. All these offer various levels of functionality and can accommodate a range of project sizes.
Key features to look for in scheduling software
When it comes to choosing a scheduling software, there are some key features that you should ensure it has. Here are some of the most critical ones:
- Gantt chart creation and customisation
- Resource management
- Task dependencies
- Real-time collaboration
- Integration with other business tools
- Reporting and analytics.
If you can find a tool that covers all these bases, you’ll be well on your way to more streamlined and effective project scheduling.
Best practices for effective project scheduling
As with all things, there are several best practices you can follow that will help you improve the quality of your project scheduling. Here are some of the most important ones:
Collaborate with team members
Get your team involved in the scheduling process. Their input can be invaluable in terms of providing more accurate estimates for task durations and helping you to identify potential issues. This approach can also be helpful in terms of getting your team to buy-in to the schedule.
Break large tasks into smaller, manageable pieces
Break complex tasks into smaller and more manageable subtasks. This method, called Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), makes it easier to estimate the time, track progress, and allocate resources.
Consider dependencies and constraints
Identify and document all task dependencies and project constraints. This will help you to avoid scheduling conflicts and ensure that activities are logically sequenced.
Build in buffer time for unexpected delays
Include buffer time in your schedule to account for potential delays and unforeseen events. This will give you more flexibility in your schedule and help to avoid missed deadlines.
Regularly update and communicate schedule changes
Update your schedule regularly and communicate any changes to stakeholders. Schedule reviews are a critical part of the overall scheduling process and can help you to identify potential problems early on.
Following these best practices will help you to create better project schedules and ultimately lead to better project outcomes.
Common challenges in project scheduling
No matter how hard we try, it’s unlikely that we won’t encounter a few bumps when planning and managing a schedule. By being aware of the following common issues that typically affect project schedules, we will be more prepared and able to identify and address any we might encounter along the way.
Inaccurate time estimates
The biggest and most common cause for schedule slippage is making incorrect estimates, both too optimistically and too conservatively. As with all estimates, we should refer to historic data, as well as include the team and subject matter experts to provide an input on time estimates.
Scope creep
Scope creep can easily affect the schedule by adding new requirements into a project that are not fully evaluated and understood, that require uncommitted resources, or that are not approved.
Resource conflicts
Resource allocation problems are common on projects where the same resources are shared among multiple projects and activities. To resolve resource overallocation or conflicts, we can use resource levelling techniques to smoothen the demand for resources.
Unexpected risks and issues
Issues can unexpectedly appear despite your best-planned schedules. Prepare a detailed risk management plan that will help you address potential problems and issues on time.
If you identify these issues and incorporate the ways to mitigate them into your project management process, you will become a better scheduler, and your projects will reach completion more successfully.
Conclusion
Project scheduling is a vital aspect of successful project management. By grasping key concepts, using the right tools and following best practices, project managers can create effective schedules. Developing strong scheduling skills will lead to better resource allocation, risk management and overall project success. Keep refining your techniques and you’ll be well on your way to learning the art of project scheduling.
FAQs
How often should I update my project schedule?
Your schedule should be updated on a regular basis, ideally weekly or after major milestones or changes.
What’s the difference between a milestone and a task in project scheduling?
A task is a specific work item, while a milestone is a significant point or event in the project.
How can I handle unexpected delays in my project schedule?
Reassess priorities, reallocate resources if necessary and communicate changes to stakeholders as soon as possible.
Is it better to use software or manual methods for project scheduling?
Software is usually more efficient and accurate, particularly for complex projects.
How do I prioritise tasks within a project schedule?
Consider dependencies, resource availability and overall impact on project objectives.
