Project management lessons learned
Dive into the world of project management lessons learned and transform your future endeavours. In this article, you’ll uncover the key benefits of reflecting on past experiences, gaining valuable insights, and improving your project management skills.

Introduction
In the world of project management, one key element that often distinguishes success from failure is the ability to extract and apply valuable insights from past experiences. This practice, known as lessons learned, involves the identification, analysis, and subsequent utilisation of experiences to better inform future actions and decision-making.
By leveraging the knowledge gained from past mistakes and successes, organisations and project managers can significantly improve their project outcomes, reduce risks, enhance team performance, and increase overall efficiency. In this article, we will embark on a comprehensive exploration of lessons learned, delving into the process of their identification, documentation, analysis, storage, and application, as well as best practices and potential challenges..
After completing this reading, you will have a complete understanding of how to successfully incorporate a lessons learned system into your organisation, paving the way for continuous improvement and project success.
The lessons learned process
The lessons learned process is a structured approach designed to help project teams capture, document, analyse, and utilise valuable insights from past experiences. By adhering to this methodical process, project managers and their teams can enhance their project performance, learn from past mistakes, and increase the probability of project success.
Five steps of the lessons learned process
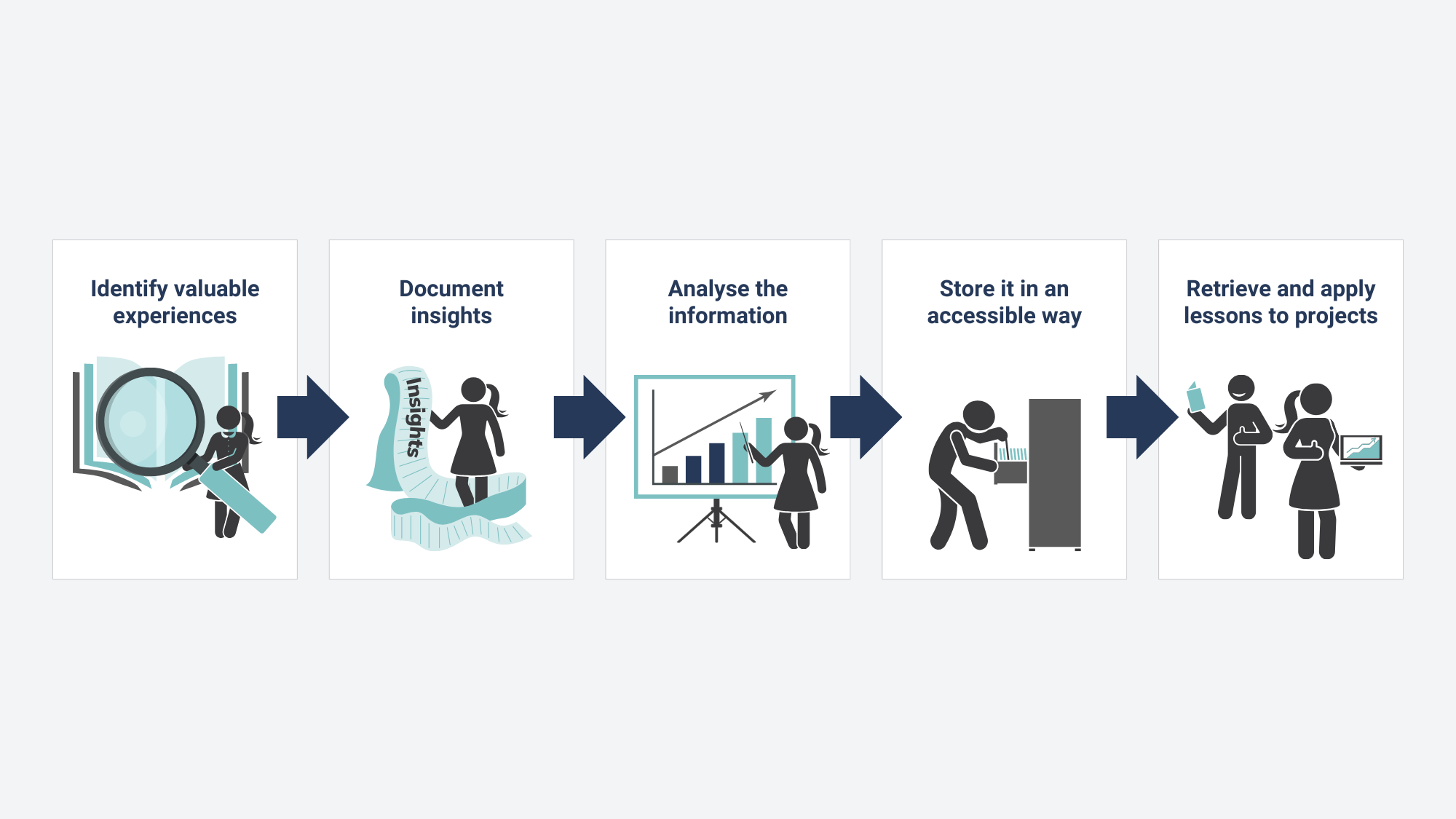
Lessons learned process diagram
- Identify: The first step in the process involves recognising and pinpointing valuable experiences and insights throughout the project life cycle. It is crucial to encourage team members to note successes and challenges as they occur.
- Document: Once identified, these lessons must be recorded in a clear, concise, and accessible manner, usually by using standardised templates or forms.
- Analyse: The documented lessons should then be examined to understand the root causes, identify patterns, and determine potential implications for future projects.
- Store: The analysed lessons should be stored in a centralised, easily accessible location, such as a database, shared drive, or specialised knowledge management system.
- Retrieve: Finally, the lessons should be retrieved and applied to current or future projects as needed. This step is essential to ensure the full value of the lessons learned process is realised.
When to capture lessons learned
Capturing lessons learned is most effective when done at the following times:
- End of project: Conducting a comprehensive review at the conclusion of the project allows for a holistic evaluation of the entire project life cycle. This timing can provide valuable insights into overall project performance and outcomes.
- End of each phase: Reviews at the end of each project phase enable teams to capture fresh insights and lessons while the information is still clear in everyone’s minds.
- Real-time learning: Encouraging the ongoing capture of lessons as they occur can help prevent valuable insights from being lost due to time lapses or fading memories.
By adhering to this structured approach and capturing lessons at these strategic moments, project teams can establish a robust knowledge base. This resource will be invaluable for improving project management practices, enhancing decision-making, and increasing the likelihood of project success.
Remember, the lessons learned process is not a one-time event but a continuous cycle of improvement. Regularly practising and refining this process can lead to substantial advancements in project management capabilities and overall organisational performance.
Identifying lessons learned
Effective identification of lessons learned is a crucial step in capitalising on the value of project experiences. This process requires careful preparation and skilled facilitation of lessons learned sessions.
Preparing for lessons learned sessions
Project surveys
Before the session, team members should be asked to complete project surveys. These surveys are designed to encourage reflection on project experiences and gather initial thoughts on successes, challenges, and other aspects of the project. They will also provide a foundation for more in-depth conversations during the lessons learned session.
Categorising lessons learned
Lessons should be organised into specific categories to help with analysis and future retrieval. Common lesson categories include:
- Project management processes
- Technical challenges
- Communication
- Resource allocation
- Risk management.
Conducting lessons learned sessions
Facilitation techniques
Facilitating productive lessons learned sessions can be achieved by using the following techniques:
- Employ a neutral facilitator to maintain objectivity
- Encourage open and honest communication
- Use brainstorming techniques to generate ideas
- Utilise visual aids such as mind maps or whiteboards to stimulate discussion and ideation.
Key questions to ask
Facilitating deliberations can be guided by using the following essential questions:
- What went well in the project?
- What challenges did we face?
- How did we overcome these challenges?
- What would we do differently next time?
- What unexpected events occurred, and how did we handle them?
By focusing on these questions, you can elicit valuable insights from your team members. Remember to create an environment where all participants feel comfortable and safe to share their experiences and observations.
By investing time and effort into thoroughly preparing and skilfully facilitating lessons learned sessions, you will be able to generate a wealth of valuable insights and information. This knowledge, when properly documented and analysed, can significantly enhance future project performance and organisational knowledge.
Documenting lessons learned
Effective documentation is critical for capturing and sharing lessons learned. This section focuses on methods for producing well-structured reports and utilising tools for efficient documentation.
Creating effective lessons learned reports
Detailed reports
Detailed reports offer an in-depth look at lessons learned. Ensure these reports include:
- Project overview and background
- Lessons gathering methodology
- Categorised lessons learned
- Root cause analysis
- Recommendations for future projects.
These reports should be well-organised, concise, and easily searchable.
Executive summaries
Executive summaries provide a concise overview of key lessons. They should highlight significant findings, present actionable recommendations, and be tailored to the needs of senior management and decision-makers.
Tools for documenting lessons learned
Lessons learned input forms
Input forms help standardise lessons collection. Design a form that captures:
- Project name and date
- Category of the lesson
- Description of the situation or issue
- Impact on the project
- Recommendations for future reference.
Templates and checklists
Templates and checklists ensure consistency in documentation across projects. Provide team members with a template for the detailed report structure, a checklist of key areas to cover during lessons learned sessions, and a standardised format for documenting recommendations.
By implementing these tools and techniques, you can develop a streamlined approach to documenting lessons learned. This system will help you capture valuable insights effectively and ensure they can be easily accessed and applied to future projects.
Remember, the key is to create documentation that is both comprehensive and user-friendly to facilitate knowledge transfer throughout your organisation.
Analysing lessons learned
Analysis involves transforming lessons learned data into insights. It includes examining the information, identifying patterns, and formulating recommendations for future use.
Techniques for analysing lessons learned data
There are various approaches to maximise the value from your lessons learned data. Consider these techniques:
- Root cause analysis: Delve deep to uncover the underlying reasons for successes and failures.
- SWOT analysis: Identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats that the lessons highlight.
- Pareto analysis: Prioritise the 20% of factors that led to 80% of results.
- Affinity diagramming: Group related lessons to identify common themes.
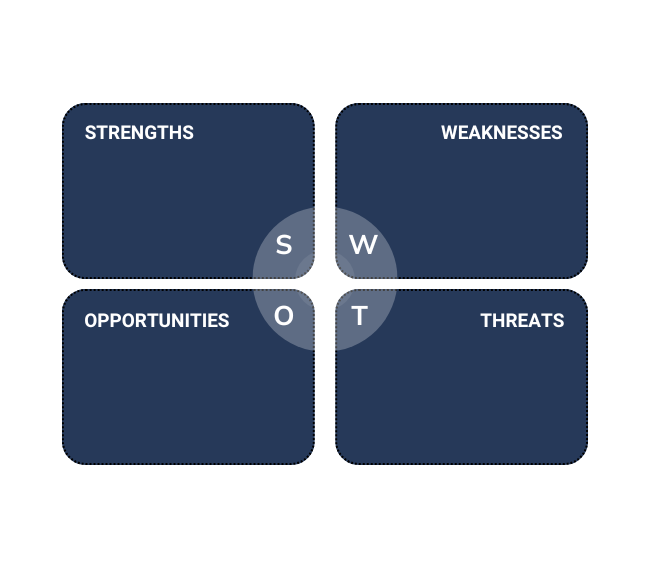
SWOT analysis diagram
Identifying trends and patterns
Search for recurring themes across several projects or stages. This can include comparing lessons from similar project types, looking at lessons across different timeframes, or analysing lessons by project role or department.
Consider using data visualisation tools like charts or heat maps to make these patterns more visible.
Generating actionable insights
Once you’ve done the analysis, turn those insights into actionable recommendations:
- Prioritise insights based on potential impact and ease of implementation.
- Create specific, measurable actions to address issues or replicate successes.
- Map the insights to existing processes or methodologies in your organisation.
- Set up a feedback loop to monitor how effective the implemented recommendations are.
Remember that the point of the analysis is not just to understand what happened, but to shape future decisions. By using these techniques, you can take lessons learned from past projects and turn them into tools for improvement. This level of analysis and critical thinking will allow your organisation to continually adapt its project management approach based on real-life experiences.
Storing and retrieving lessons learned
To effectively use lessons learned, you must have a system for storing and retrieving them. This section provides guidance on setting up an efficient process.
Creating a centralised lessons learned repository
A central repository should be the single source of truth for all lessons learned in your organisation. When building this repository, it’s important to choose a platform that works well with your existing project management tools. Use a consistent structure and categorisation system, so the lessons are well-organised. Plan for the repository to be scalable so you can add new projects and insights over time.
Implementing effective search and retrieval systems
Make sure that lessons are easily discoverable. This can be done by implementing a good search function with filters based on project type, date, and category. Use a tagging system to identify key themes and topics, which will allow users to find relevant information quickly. You can also add an option for users to rate the usefulness of a lesson to help surface the most valuable insights. These features will help increase the accessibility and usefulness of the stored knowledge.
Ensuring accessibility and usability of stored lessons
Encourage everyone to use the lessons learned repository by making it accessible and easy to use. This includes creating user-friendly interfaces on both desktop and mobile platforms. Role-based access control can help protect sensitive information while still providing appropriate access. Regularly curate the content to keep it up-to-date and valuable. Conduct training sessions on how to use the repository so that everyone can get the most out of this resource.
Creating a well-organised, easily searchable, and accessible repository will ensure your organisation can effectively leverage past experiences. This will turn lessons learned from being static records into resources that actively improve decision-making and project outcomes across your organisation.
Leveraging lessons learned for future projects
The real power of lessons learned lies in how they are applied to future projects. In this part, we’ll explore strategies and techniques for leveraging lessons learned effectively to improve project outcomes and drive organisational success.
Incorporating lessons learned into project planning
Incorporating lessons learned into your project planning process is a crucial step in ensuring that past experiences inform future work. To do this, review relevant lessons learned when starting a new project. Make a lessons learned review a standard part of project kick-off meetings and assign team members to research and present applicable lessons to the group. This practice ensures that lessons learned are not just documented but actively inform your project strategies.
Update project templates and checklists based on lessons learned to embed these insights into your standard operating procedures.
Sharing lessons learned across the organisation
Maximising the value of lessons learned involves creating a culture that values knowledge sharing and continuous learning. Establish regular forums or platforms for teams to exchange and disseminate key lessons learned. Integrate lessons learned into training programmes and new employee onboarding processes to spread valuable insights across the organisation.
Encourage and reward individuals and teams that actively apply and share lessons learned to reinforce their importance.
Continuous improvement through lessons learned
Continuous improvement is key to organisational growth and development. Implement a feedback loop to track the effectiveness of applied lessons learned. Regularly review and update your lessons learned repository to ensure it remains relevant and useful. Encourage teams to challenge existing practices and standards based on new insights and insights to promote innovation and adaptation.
Organisationally, use lessons learned data to inform strategic decision-making, ensuring that the company’s direction is shaped by real-world experiences and outcomes.
By actively leveraging lessons learned, you can turn past experiences into valuable assets for future success. This proactive approach to project management not only improves individual project outcomes but also cultivates a culture of continuous learning and improvement throughout the organisation.
Remember, collecting lessons is just the first step; the real value lies in how you apply them systematically to drive tangible improvements in project practices and outcomes.
Challenges and best practices
Implementing an effective lessons learned process can be difficult, but being aware of the common challenges and best practices can help organisations overcome these issues and get the most value from their experiences.
Common obstacles in implementing lessons learned processes
Many organisations face challenges such as time constraints, which often relegate lessons learned to a low-priority task. Cultural resistance to admitting mistakes or sharing failures can also impede the process. Inconsistent documentation and poor knowledge management systems frequently lead to lost or inaccessible lessons.
Strategies for overcoming challenges
To overcome these obstacles, organisations should integrate lessons learned activities into project timelines and allocate dedicated resources. Promoting a blame-free culture that values learning and improvement can encourage more open sharing of experiences. Standardising documentation processes and implementing user-friendly knowledge management systems can also help capture and retrieve lessons more effectively.
Best practices for maximising the value of lessons learned
To maximise the value of your lessons learned process, consider making it a continuous activity throughout the project lifecycle, rather than a one-time event. Involve all stakeholders in the lessons learned process, not just the project team, to gain a more comprehensive perspective. Use a variety of methods to collect lessons, such as surveys, interviews, and workshops, to capture a diverse range of insights. Ensure that documented lessons are specific, actionable, and relevant to future projects to increase their utility. Regularly review and update your lessons learned repository to keep it relevant and valuable over time.
Measuring the impact of lessons learned
Ensuring the effectiveness of your lessons learned process requires you to measure its impact on project performance and organisational growth. This section will focus on key performance indicators and evaluation methods for assessing the value of your lessons learned initiatives.
Key performance indicators for lessons learned processes
Consider tracking the following KPIs to measure the success of your lessons learned efforts:
- Number of lessons captured per project
- Percentage of lessons applied to subsequent projects
- Reduction in recurring issues across projects
- Improvement in project success rates
- Time saved through application of lessons learned.
Methods for evaluating the effectiveness of lessons learned initiatives
To evaluate the impact of your lessons learned programme, try the following techniques:
- Conduct surveys to measure team members’ perceived value of the process
- Compare project outcomes before and after implementing lessons learned initiatives
- Track the frequency of accessed lessons in your repository
- Analyse the correlation between applied lessons and project success metrics
- Perform regular audits to ensure lessons are being consistently captured and utilised.
By measuring the impact of your lessons learned process systematically, you can demonstrate its value to stakeholders and identify areas for improvement. This data-driven approach ensures that your organisation continues to refine and enhance its knowledge management practices.
Conclusion
The lessons learned process is a vital component for organisational improvement and project success. By implementing a structured approach to identifying, documenting, analysing, storing, and retrieving valuable insights, organisations can significantly enhance their project management practices and drive continuous improvement.
A culture of continuous learning is paramount for the success of lessons learned activities. Cultivating an environment that encourages open communication, values experiential knowledge, and promotes sharing and applying insights across projects and teams will maximise the potential benefits of this process.
To unlock the full power of lessons learned, organisations must commit to making these activities an integral part of the project lifecycle and create a blame-free environment where team members feel safe to reflect honestly. Additionally, investing in user-friendly systems for capturing and accessing lessons, as well as regularly measuring and evaluating the effectiveness of lessons learned initiatives, will ensure the sustainability and continuous improvement of this valuable practice.
By embracing the principles and implementing effective lessons learned processes discussed in this guide, organisations can drive continuous improvement, reduce the recurrence of issues, and ultimately achieve greater project success. Start improving your lessons learned practices today to secure a more efficient and effective project management future.
FAQs
How often should lessons learned sessions be conducted?
Ideally, at the end of each project phase and upon project completion. For longer projects, consider quarterly sessions to capture insights while they’re fresh.
What’s the difference between lessons learned and project post-mortems?
Lessons learned focus on ongoing improvement throughout the project lifecycle. Post-mortems typically occur at project end and may have a broader scope, including overall project performance evaluation.
How can we encourage team members to actively participate in lessons learned sessions?
Create a blame-free environment, emphasise the value of learning, and demonstrate how insights are applied. Consider using anonymous submission methods for sensitive topics.
What are some effective tools for capturing lessons learned in real-time?
Project management software with built-in features, dedicated mobile apps, or simple shared documents. The key is accessibility and ease of use for team members.
How can we ensure lessons learned are actually applied to future projects?
Integrate lessons review into project kick-off meetings, update project templates based on learnings, and assign responsibility for implementing specific lessons.
What role does leadership play in promoting a culture of lessons learned?
Leaders should actively participate in sessions, allocate resources for the process, and visibly apply insights in decision-making to demonstrate the value of lessons learned.
How can we make lessons learned sessions more engaging and productive?
Use varied formats like workshops or gamification, focus on specific themes, and ensure sessions result in actionable outcomes to maintain engagement.
What are some common pitfalls to avoid when implementing a lessons learned process?
Avoid treating it as a checkbox exercise, neglecting to follow up on actions, or allowing sessions to become blame games. Ensure the process is consistently applied across all projects.
Infographic