Introduction
Project management is a challenging process that is prone to many possible failures. Risk management is a key aspect of project management that can help increase the likelihood of project success. This involves the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that can threaten the project.
In this article, we will explore some of the risks that can arise on projects and how to deal with them effectively. We will discuss the following topics:
- The definition and importance of understanding project risks
- The different types of common project risks
- The process of risk management on projects
- The tools and techniques used in risk management
- The strategies for effective risk mitigation
- The best practices for successful risk management on projects.
By the end of this article, you will be able to:
- Identify potential risks on your projects
- Apply effective risk management strategies
- Improve the chances of your project’s success.
You can also learn about project risk management on a project management course such as PRINCE2 course or an APM course.
Let’s begin and explore the world of project risk management and how to protect your projects from potential risks.
Understanding project risks
Definition of project risk
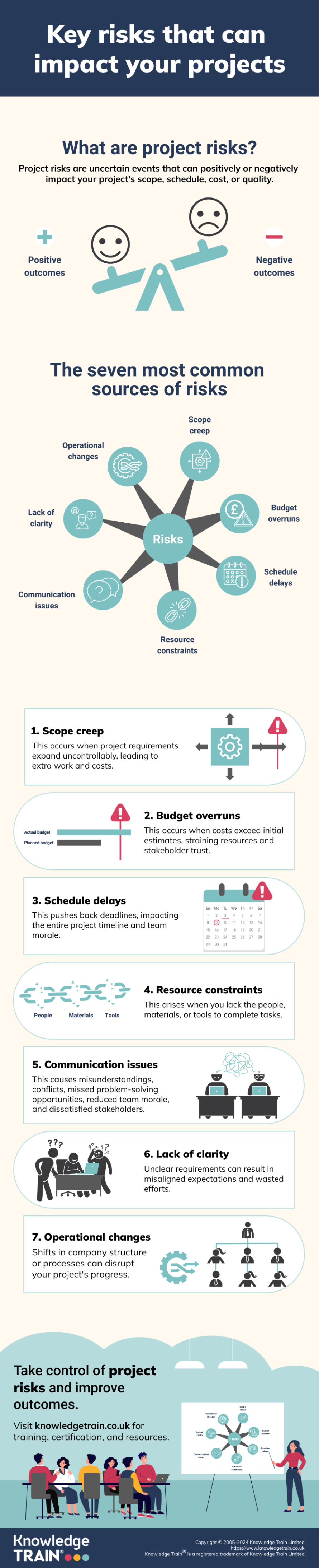
A project risk refers to an uncertain event or condition that, if it occurs, has the potential to either positively or negatively affect the outcome of a project. Risks can impact project objectives such as scope, schedule, cost, or quality. Examples of project risks include changes in customer requirements, budget constraints, delays in schedules, technical issues, resource shortages, and more.
Types of project risks
Project risks can be classified into various categories, including:
- Internal risks: These risks originate from within the project or the organisation itself. They can be related to factors such as team dynamics, resource availability, or management decisions.
- External risks: These risks arise from factors outside the project’s control, such as economic conditions, regulatory changes, natural disasters, or market trends.
- Technical risks: Technical risks are associated with the technology or methodologies used in the project. They may involve issues like software glitches, hardware failures, integration challenges, or inadequate technical expertise.
- Financial risks: Financial risks impact the project’s budget, funding, or financial resources. They can include factors like unexpected cost overruns, currency fluctuations, or inadequate financial planning.
- Operational risks: Operational risks affect the day-to-day functioning of the project. They can encompass issues like human errors, process inefficiencies, supply chain disruptions, or equipment failures.
- Strategic risks: Strategic risks influence the project’s alignment with the organisation’s overall business goals. They may involve risks related to changing market demands, competitive pressures, or organisational changes.
Impact of risks on project success
Risks can have a variety of impacts on a project’s success:
- Positive effects: These could include opportunities for innovation or efficiency improvements
- Negative effects: These could lead to delays, cost overruns, or quality issues.
Effective risk management is important for minimising negative impacts and maximising the potential for opportunities and overall project success.
By identifying and assessing risks, project managers can develop contingency plans and take proactive steps to mitigate potential problems. This helps increase the chances of achieving project goals and delivering value to stakeholders.
Common project management risks
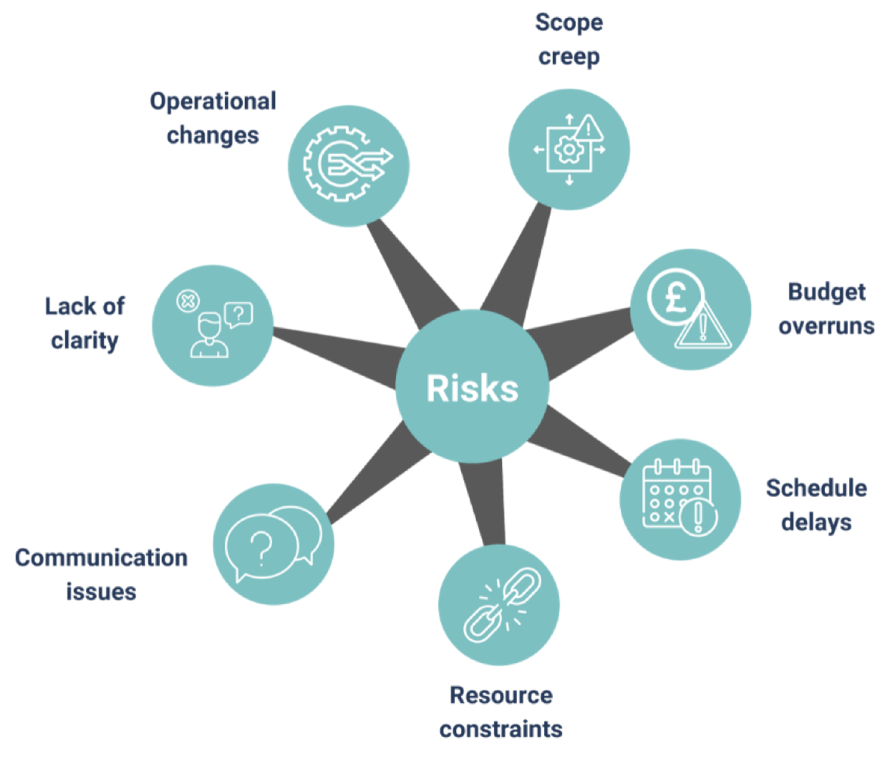
Scope creep
Common causes
Scope creep is the uncontrolled expansion of a project’s scope without corresponding adjustments to time, budget, and resources. Common causes of scope creep include ambiguous initial requirements, lack of change control processes, Stakeholder pressure for additional features, and insufficient stakeholder engagement.
Impact
Scope creep can have several impacts on a project:
- It can increase the project’s duration, require more resources and increase costs
- It can lead to delays and missed deadlines
- It can cause the project to lose focus and drift away from its original objectives
- It can lead to team burnout and demotivation.
To prevent scope creep, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the project’s objectives and requirements, and to establish change control processes to manage and approve any changes to the project scope.
Budget overruns
Common causes
Budget overruns occur when the actual cost of a project exceeds the initially allocated budget. Common causes of budget overruns include inaccurate cost estimation, scope changes, unforeseen expenses, and poor resource management.
Impact
Prevent budget problems by performing a detailed cost analysis and ensuring financial reporting is transparent throughout the project.
Schedule delays
Common causes
Schedule delays can occur due to a variety of reasons:
- Unrealistic time estimates
- Resource unavailability
- Dependency conflicts
- External factors (e.g. weather, supplier delays).
Impact
Schedule delays can lead to missed deadlines and milestones, increased costs due to prolonged project duration, reduced stakeholder satisfaction and potential loss of competitive advantage.
To address time-related risks, implement effective project scheduling techniques and regularly monitor project progress.
Resource constraints
Types of resource risks
Resource risks can take various forms, such as:
- Skill shortages
- Equipment or material unavailability
- Insufficient funding
- Limited time availability.
Impact on project performance
Resource constraints can result in reduced productivity, compromised quality of deliverables, increased stress on team members and potential project delays.
Conduct thorough resource planning and maintain open communication with stakeholders to proactively address resource-related issues.
Communication issues
Importance of effective communication
Effective communication is vital for project success. It facilitates alignment of project objectives, timely issue resolution, stakeholder engagement and buy-in and efficient team collaboration.
Consequences of poor communication
Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings and conflicts, missed opportunities for problem-solving, reduced team morale and productivity and stakeholder dissatisfaction.
Establish clear communication channels and protocols to promote open and transparent dialogue throughout the project.
Lack of clarity
Sources of unclear requirements
Unclear requirements can stem from ambiguous project objectives, insufficient stakeholder input, lack of detailed documentation and changing business needs.
Effects on project outcomes
Lack of clarity can lead to misaligned expectations, rework and wasted resources, delayed decision-making and compromised project quality.
Invest time in gathering and documenting clear requirements and maintain ongoing stakeholder engagement to ensure alignment.
Operational changes
Types of operational risks
Operational changes can include:
- Organisational restructuring
- Process modifications
- Technology upgrades
- Regulatory changes.
Impact on project execution
Operational changes can affect projects by disrupting established workflows, requiring additional training or resources, altering project priorities and necessitating scope or timeline adjustments.
Stay informed about potential organisational changes and maintain flexibility in project planning to accommodate operational shifts.
By knowing about common project management risks, you can make specific plans to help prevent or overcome them. In addition, proactive risk management involves:
- Regular risk assessments
- Clear communication with stakeholders
- Robust change management processes
- Continuous monitoring and adaptation.
Keep in mind that effective risk management is an ongoing process that needs careful monitoring and flexibility throughout the project. If you plan and work for these common risks, you will be able to increase the probability of success in your project.
Risk management process
Risk identification
The first step in risk management is to identify potential risks that could impact your project. Some common techniques include:
- Brainstorming with team members
- Reviewing historical information from similar projects
- Conducting stakeholder interviews
- Analysing project documentation.
Create a risk register to document all identified risks.
Risk assessment and prioritisation
After identifying risks, assess their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. Tools you can use include:
- Risk matrix: Plot risks on a chart based on their probability and impact
- Quantitative analysis: Assign numerical values to risks
- Qualitative analysis: Categorise risks based on severity.
Prioritise risks based on their potential impact.
Risk response planning
For each prioritised risk, develop a response strategy. Common responses include:
- Avoidance: Eliminate the threat by changing project plans
- Mitigation: Reduce the probability or impact of the risk
- Transfer: Shift the risk to a third party (e.g. insurance)
- Acceptance: Acknowledge the risk and prepare contingency plans.
Document your response strategies in a risk management plan.
Risk monitoring and control
Continuously monitor risks throughout the project lifecycle. This includes:
- Regular risk reviews and updates
- Tracking risk triggers and early warning signs
- Implementing planned responses when necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of risk responses.
Adjust your risk management approach as needed based on new information and changing project conditions.
By following this structured process, you can effectively manage risks and increase your project’s chances of success.
Tools and techniques for project risk management
Risk register
A risk register is a document that lists all identified risks along with their potential impact and planned mitigation. Components to include are:
- Risk description
- Probability and impact assessment
- Risk owner
- Mitigation strategies
- Contingency plans.
Maintain your risk register throughout the project, regularly updating it as needed.
SWOT analysis
SWOT analysis is used to identify factors that may impact your project:
- Strengths: Project advantages
- Weaknesses: Areas for improvement
- Opportunities: Potential benefits
- Threats: Possible risks.
Performing a SWOT analysis gives you a well-rounded view of your project’s risk landscape.
Brainstorming sessions
Organise structured brainstorming sessions with your team to identify potential risks. Encourage open discussion and creative thinking. Techniques you can use include:
- Nominal group technique
- Affinity diagramming
- Mind mapping.
Brainstorming sessions can help identify risks that might be overlooked otherwise.
Project management software
Project management software is a valuable tool for helping to streamline your risk management processes. Features to consider include:
- Risk tracking and monitoring
- Automated alerts for risk triggers
- Collaboration tools for team communication
- Reporting capabilities for stakeholder updates.
Project management software can greatly improve your ability to manage risks throughout your project.
Strategies for mitigating common project risks
Preventing scope creep
- Clearly define project boundaries and scope during the planning stage
- Implement a change control process to evaluate and approve scope changes
- Communicate the impact of scope changes to all stakeholders.
Managing budget risks
- Accurate cost estimation and inclusion of contingency reserves
- Regular budget monitoring and reporting
- Cost control measures and prioritisation of expenses.
Addressing schedule delays
- Utilise critical path analysis to identify key milestones and dependencies
- Build buffer time into project schedules
- Regularly review and adjust timelines based on progress updates.
Optimising resource allocation
- Conduct thorough resource planning at the outset of the project
- Utilise resource levelling techniques to balance workloads
- Maintain a skills inventory to quickly identify and address skill gaps.
Improving communication
- Establish clear communication channels and protocols
- Schedule regular team meetings and stakeholder updates
- Utilise collaboration tools to facilitate information sharing.
Ensuring clarity in project requirements
- Conduct thorough requirements gathering sessions with stakeholders
- Create detailed, unambiguous project specifications
- Implement formal requirements review and approval process.
Adapting to changes
- Stay informed of potential changes within the organisation
- Build flexibility into project plans to accommodate operational shifts
- Develop contingency plans for significant operational disruptions.
By following these tips, you can avoid most of the common pitfalls that can cause problems in your projects. Keep in mind that risk management is a continuous process. It is important to revisit the steps in this process as you continue with your project.
Best practices for effective risk management
Proactive approach to risk identification
- Try to spot potential risks at the start of a project
- Ask team members to raise red flags as soon as possible
- Look at past data and apply any relevant lessons learnt.
Regular risk assessment
- Hold regular check-ins to review identified risks and their status
- Re-evaluate risks as the project progresses and circumstances change
- Revise risk mitigation plans as necessary.
Stakeholder involvement in risk management
- Include stakeholders in identifying and assessing risks
- Keep stakeholders informed of risk management plans and progress
- Seek stakeholder input on risk mitigation strategies.
Continuous learning and improvement
- Record lessons learnt from risk management successes and failures
- Share information with other project teams to improve organisational risk management
- Invest in ongoing training and development of risk management skills.
Follow these tips to help you establish a positive risk management culture and improve project success.
Conclusion
Recap of key points
Effective project risk management is a multi-faceted approach that involves identifying and assessing potential risks, developing mitigation strategies, utilising appropriate tools and techniques, and implementing best practices for continuous improvement.
These elements form a comprehensive framework for managing uncertainties in project management.
Importance of ongoing risk management
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance, regular reassessment and adaptation to changing project conditions.
By prioritising risk management throughout the project lifecycle, you increase the likelihood of project success. Remember, proactive risk management is an investment in your project’s future, safeguarding its objectives and deliverables.
FAQs
What is the difference between internal and external project risks?
Internal risks are those that originate within the project or organisation, while external risks stem from outside factors beyond the direct control of the project team.
How often should risk assessments be conducted during a project?
Risk assessments should be conducted regularly throughout a project, often at predetermined intervals or key project milestones. Monthly risk assessments are typical for most projects.
What role do stakeholders play in project risk management?
Stakeholders can provide valuable input in identifying risks, assessing their potential impact, and helping to develop risk mitigation strategies.
Can all project risks be eliminated?
No, not all project risks can be eliminated. The focus should be on effectively managing and mitigating risks.
How can small teams effectively manage project risks with limited resources?
Small teams can prioritise risks based on their potential impact, use simple risk assessment tools, and leverage the diverse expertise of team members to ensure comprehensive risk management.
Infographic