Project management methods: a guide to modern approaches
Key takeaways
Choose a project approach that fits the work, the team, and the organisation.
- Waterfall suits stable requirements and benefits from clear phases, documentation, and predictable planning.
- Agile methods prioritise rapid, iterative delivery, close collaboration, and frequent feedback to handle change.
- Lean improves delivery by maximising customer value and removing waste, and Lean Six Sigma adds data-driven quality control.
- Hybrid approaches like Scrumban blend structure and flow to cope with shifting priorities and unexpected work.
- Method selection should reflect project complexity, stakeholder involvement, risk, and organisational culture, and be reviewed at key milestones.
Introduction
Running a modern business requires that certain tasks are coordinated in a way that increases chances of getting results. Project management methodology is a set of rules and processes that are implemented by teams in order to plan, develop, and deliver project outcomes. In this way, business people can make the most of the project to achieve business goals.
Choosing the right one is important for several reasons: the methodology should be applicable to your teams’ strong suits and their project needs it should also be helpful in communication and collaboration it needs to improve the process of resource allocation and risk management and, finally, it is likely to increase the chances of project success.
This comprehensive guide will look at the most relevant project management methodologies, including:
- Traditional approaches like waterfall
- Agile methodologies such as Scrum and Kanban
- Lean project management principles
- Hybrid and adaptive frameworks.
We will review the strengths and weaknesses of each project management method, enabling you to select the most appropriate one for your next endeavor. Gain a better understanding of these methods, and it will be easier for you to lead your team to victory.
Core project management philosophies
Project management methodologies may be classified into two broad categories, based on their fundamental philosophies. These are linear and iterative. It’s important to be aware of these core strategies when choosing the best approach for your project.
Linear (Waterfall) approach
Description and key principles
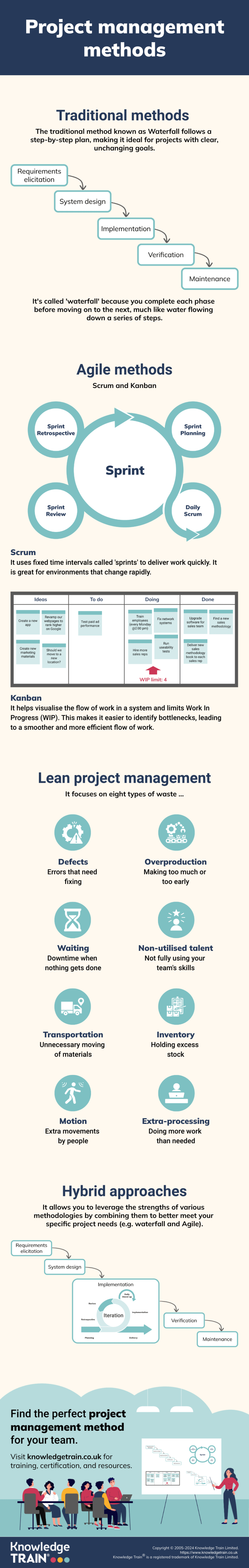
The Waterfall strategy is a linear approach where a project is broken down into distinct phases, and each phase is completed before progressing to the next. Core tenets of this approach include detailed upfront planning, comprehensive documentation at each phase, rigorous change control processes, and a strong emphasis on following the planned path.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Clear structure and defined milestones
- Well-defined deliverables
- Easier costs and timelines estimation.
Disadvantages:
- Limited flexibility to accommodate changes
- Late identification of issues or misalignments
- Potentially longer development cycles.
Iterative (Agile) approach
Description and key principles
Agile methodologies, on the other hand, emphasise flexibility, collaboration, and the rapid delivery of working products. Core tenets of Agile approaches include iterative development cycles (known as sprints), continuous feedback and adaptation, close collaboration with stakeholders, and a focus on delivering value early and frequently.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Adaptability to changing requirements
- Early and frequent delivery of usable products
- Increased stakeholder satisfaction
- Quicker identification and resolution of issues.
Disadvantages:
- Risk of scope creep
- Challenges in estimating overall project timelines
- Requires highly skilled and self-motivated team members.
It’s worth noting that choosing between linear and iterative strategies depends on several factors, such as project complexity, stakeholder involvement, and the team’s capabilities. Additionally, some projects may benefit from a hybrid approach that combines elements of both strategies to leverage their respective strengths.
Traditional project management methodologies
In this article, we will dive deep into several traditional project management methodologies. These have been in use for years, and if you are new to the field or are simply curious to learn more, read on!
Waterfall
Process and stages
Waterfall methodology follows a linear and sequential approach consisting of the following stages:
- Requirements gathering
- Design
- Implementation
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance.
Each stage must be completed before proceeding to the next, with an emphasis on documentation and clear milestones.
Best use cases
Construction projects, manufacturing processes, large-scale infrastructure projects and projects with well-defined and stable requirements are particularly suitable for Waterfall.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Clear structure and timeline
- Easy to understand and manage
- Detailed documentation at each stage.
Cons:
- Limited flexibility for changes
- Late identification of issues
- Potentially lengthy development cycles.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
Key concepts and implementation
CPM is a scheduling technique for project activities. It involves identifying all necessary tasks, task dependencies, calculating the longest path of planned activities, and determining the minimum project duration.
Suitable projects and industries
CPM is commonly used in construction projects, product development, research initiatives, and event planning.
PRINCE2 (PRojects IN Controlled Environments)
Framework overview
PRINCE2 is a process-based method that emphasises organisation and control. Its key features include division into manageable stages, defined roles and responsibilities, product-based planning approach and a strong focus on business justification.
When to use PRINCE2
PRINCE2 is well-suited for large-scale government projects, IT implementations, business transformations and projects with a need for strict governance.
Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK)
Core principles and processes
PMBOK is a comprehensive guide that offers best practices across five process groups:
- Initiating
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Closing.
It also encompasses ten knowledge areas, including scope, time, cost, and quality management.
Applications in various industries
PMBOK principles can be applied in information technology, healthcare, finance and banking, engineering and construction, and education industries, among others.
These traditional methodologies provide reliable frameworks for managing projects. They work best in situations where requirements are well-defined, and stability is preferred over flexibility. However, they can face challenges in rapidly changing environments or when continuous stakeholder feedback is essential.
Ultimately, the choice of methodology depends on the specific needs of your project, the capabilities of your team, and the organisational culture you operate within. In some cases, a combination of different approaches may be the most effective solution.
Agile project management methodologies
Agile methodologies emphasise flexibility, collaboration, and rapid delivery of value. These approaches have gained significant popularity, particularly in software development and other dynamic industries.
Scrum
Roles, events, and artifacts
Scrum is a lightweight framework that helps teams work together effectively. It consists of:
| Roles | Events | Artifact |
| Product Owner | Sprint Planning | Product Backlog |
| Scrum Master | Daily Scrum | Sprint Backlog |
| Development Team | Sprint Review | Review Increment |
| Sprint Retrospective |
Sprint planning and execution
Scrum operates in time-boxed iterations known as Sprints, typically ranging from 1 to 4 weeks. During each Sprint, the team commits to delivering a set of features.
Benefits and challenges
Benefits:
- Improved product quality
- Increased stakeholder satisfaction
- Better team collaboration.
Challenges:
- Requires cultural shift
- Potential for scope creep
- Difficulty in estimating long-term projects.
Kanban
Visualising workflow with Kanban boards
Kanban uses visual boards to represent work items as they move through different stages of completion.
Principles of Kanban
Key principles include:
- Visualise the workflow
- Limit Work In Progress (WIP)
- Manage flow
- Make process policies explicit
- Implement feedback loops.
Industries benefiting from Kanban
Kanban is versatile and can be applied in various sectors, including software development, marketing and design, human resources, and manufacturing.
Extreme Programming (XP)
Key practices and values
XP emphasises technical excellence and customer satisfaction. Core practices include pair programming, test-driven development, continuous integration, and small, frequent releases.
Best scenarios for XP implementation
XP is particularly effective for projects with changing requirements, small to medium-sized development teams, and environments that value close collaboration with customers.
Crystal
Family of methodologies
Crystal is a family of Agile methodologies, each named after a precious gemstone. Popular variants include:
- Crystal Clear
- Crystal Yellow
- Crystal Orange
- Crystal Red.
Each variant is designed for different team sizes and project criticality.
Core principles and adaptability
Crystal methodologies share common principles, such as frequent delivery, reflective improvement, osmotic communication, personal safety and focus.
The framework is highly adaptable, allowing teams to customise their approach based on project needs.
Feature Driven Development (FDD)
Five processes of FDD
FDD consists of five main processes:
- Develop an overall model
- Build a features list
- Plan by feature
- Design by feature
- Build by feature
Advantages for client-focused projects
FDD offers several benefits for client-centric projects:
- Regular, tangible progress
- Early detection of errors
- Accurate status reporting
- Scalability for larger projects.
Agile methodologies offer numerous advantages, including increased flexibility, faster delivery of value, and improved stakeholder satisfaction. However, they also present challenges, such as the need for cultural change and potential difficulties in long-term planning.
When considering an Agile approach, evaluate your team’s skills, project requirements, and organisational culture. Some projects may benefit from combining elements of different Agile methodologies or even blending Agile with traditional approaches.
Remember that successful implementation of any Agile methodology requires commitment from the entire team and support from management. Continuous learning and adaptation are key to maximising the benefits of Agile project management.
Lean project management
Origins and principles of lean
Lean is a philosophy that originated in the manufacturing industry, particularly in the production system of Toyota. The primary principle of Lean is to maximise customer value while minimising waste. Lean thinking has been adapted to other industries, including project management.
Key principles of Lean include:
- Identify value
- Map the value stream
- Create flow
- Establish pull
- Seek perfection.
Eliminating waste in project management
Lean project management is all about identifying and eliminating waste in processes. There are 8 types of waste that Lean project management focuses on:
- Defects
- Overproduction
- Waiting
- Non-utilised talent
- Transportation
- Inventory
- Motion
- Extra-processing.
By reducing these wastes, teams can improve efficiency and provide more value to stakeholders.
Lean Six Sigma
Combining Lean and Six Sigma methodologies
Lean Six Sigma combines Lean principles with Six Sigma’s data-driven approach to quality improvement. The goal is to reduce waste and variation in processes.
DMAIC process
Lean Six Sigma projects use a process called DMAIC, which stands for Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control:
- Define: Identify the problem and project goals
- Measure: Collect data on the current process
- Analyse: Identify root causes of problems
- Improve: Implement and verify solutions
- Control: Maintain the improved process.
This structured approach allows teams to systematically improve processes and reduce variability.
Lean project management provides a powerful framework for optimising project delivery. By focusing on creating value and eliminating waste, teams can achieve better results with fewer resources. When combined with Six Sigma principles, Lean offers a comprehensive toolkit for continuous improvement in project management practices.
Hybrid and adaptive methodologies
As the field of project management continues to evolve, hybrid and adaptive methodologies have emerged to meet the demands of complex and dynamic project environments. These approaches combine elements from various project management frameworks to create flexible and tailored solutions.
Scrumban (Scrum + Kanban)
Combining Scrum and Kanban principles
Scrumban is a hybrid methodology that merges Scrum’s structured sprints with Kanban’s visual workflow management. This approach retains Scrum’s iterative nature while incorporating Kanban’s principles of continuous flow and visualisation.
Benefits of the hybrid approach
The Scrumban methodology offers several advantages:
- Improved workflow visualisation
- Increased flexibility in task management
- Enhanced team collaboration
- Better handling of unexpected changes.
Dynamic Systems Development Method
(DSDM)Structured Agile approach
DSDM is a comprehensive Agile project delivery framework that emphasises the early and continuous delivery of business value. It provides a structured approach to Agile project management.
MoSCoW prioritisation technique
DSDM utilises the MoSCoW method for prioritising requirements, which includes:
- Must have
- Should have
- Could have
- Won’t have this time.
This prioritisation technique ensures that the focus remains on essential deliverables within time and resource constraints.
Adaptive Project Framework (APF)
Flexibility in uncertain environments
APF is designed to handle projects with high levels of uncertainty. It allows for continuous adaptation and adjustment as new information becomes available.
Key components of APF
APF consists of five stages:
- Project scope
- Cycle plan
- Cycle build
- Client checkpoint
- Post-cycle review.
These stages promote iterative development and frequent stakeholder involvement.
Hybrid and adaptive methodologies provide tailored solutions for complex and dynamic projects. By combining elements from various approaches, teams can create flexible frameworks that address specific project needs and organisational cultures.
Choosing the right project management methodology
Factors to consider
- Project complexity and size: Larger, complex projects may benefit from a more structured approach like waterfall or PRINCE2.
- Team size and expertise: Smaller, highly skilled teams may thrive using Agile methods.
- Industry standards and requirements: Some industries have established preferences or regulations for specific methodologies.
- Stakeholder involvement: Iterative methods like Scrum can work well when stakeholder involvement is high.
- Risk tolerance and adaptability: Adaptive methodologies are more appropriate when the project requirements are uncertain or evolving.
Importance of organisational culture fit
The methodology you choose should align with your organisation’s culture, values, and working style. Mismatch can result in resistance and decreased effectiveness.
Remember, there is no one-size-fits-all methodology. Consider your project’s unique requirements and be flexible enough to adapt your approach as the project evolves.
Conclusion
Recap of key methodologies
We’ve covered various project management methodologies, including traditional waterfall, PRINCE2, and Agile methodologies like Scrum and Kanban. We also touched on hybrid approaches like Scrumban that combine elements of different methodologies.
Importance of continuous learning and adaptation
Project management is an ever-evolving field. To be successful, project managers must stay updated on new methodologies, tools, and industry best practices. The ability to adapt your approach based on the specific needs of your projects and teams is crucial.
It’s important to emphasise that no methodology is perfect for every situation. The key to success lies in understanding different methodologies and choosing the most appropriate one for each unique project.
FAQs
What is the difference between Agile and Waterfall methodologies?
Agile methodologies are iterative and flexible, while Waterfall is linear and sequential.
How do I know which project management methodology is best for my team?
Consider factors like project complexity, team size, industry standards, and organisational culture.
Can I combine different project management methodologies?
Yes, hybrid methodologies like Scrumban incorporate elements from multiple methodologies.
What are the key benefits of using an Agile methodology?
Agile methodologies offer benefits such as flexibility, faster delivery, and improved stakeholder satisfaction.
How does Lean project management differ from traditional approaches?
Lean focuses on eliminating waste and maximising value, while traditional methods emphasise detailed planning and control.
What role does software play in implementing project management methodologies?
Software tools facilitate methodology implementation by enabling communication, task tracking, and resource management.
How often should I reassess my chosen project management methodology?
It’s a good practice to regularly evaluate the effectiveness of your methodology, especially during project milestones or when encountering new challenges.
Remember, the best project management methodology is the one that suits your project’s specific needs and your team. Don’t be afraid to adapt and refine your approach as necessary.
Infographic