Introduction to PESTLE analysis
Definition and purpose
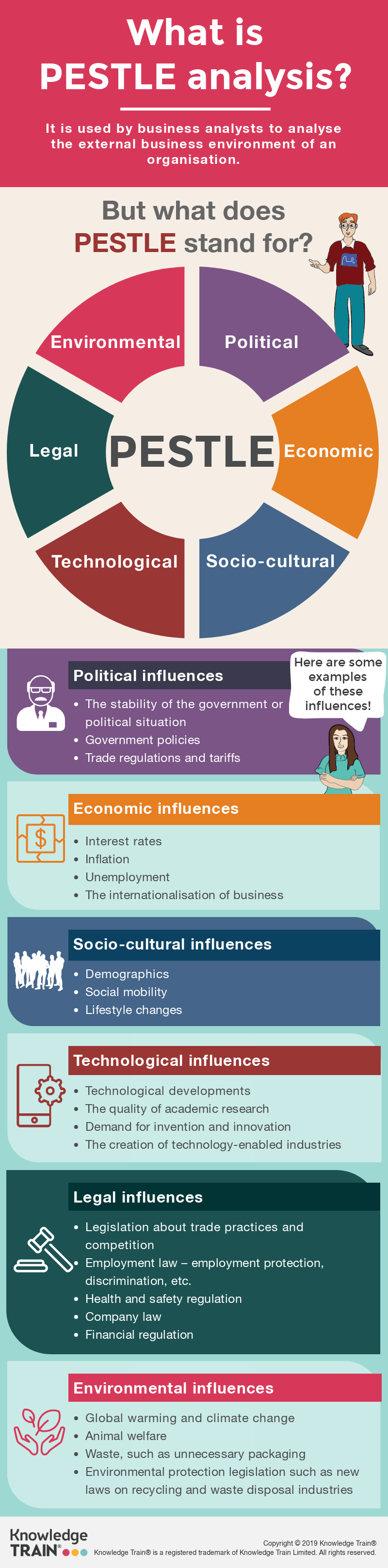
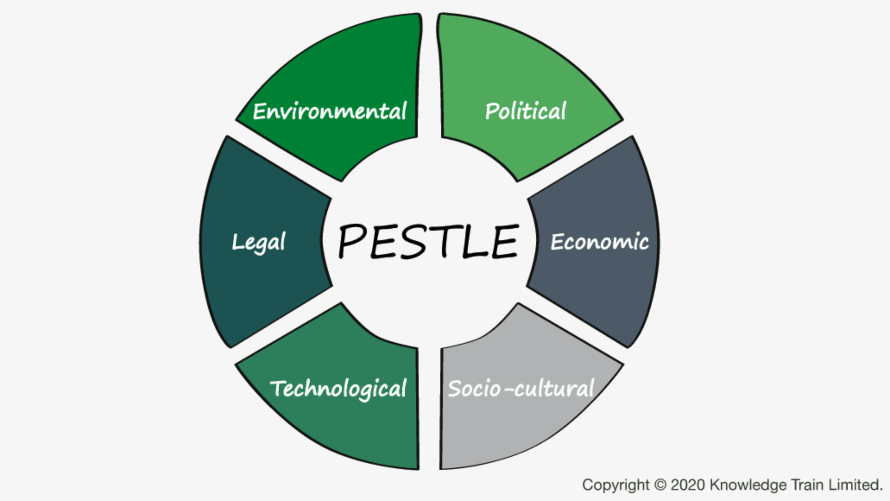
PESTLE analysis is a strategic tool used to identify and assess the external factors that can impact a business. It stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors. The primary purpose of PESTLE analysis is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the macro-environmental conditions affecting an organisation. By evaluating these external forces, businesses can anticipate changes and adapt their strategies accordingly. This proactive approach aids in mitigating risks and capitalising on potential opportunities.
Evolution from PEST to PESTLE
The framework began as ETPS, created by Francis Aguilar in 1967, before being rearranged to PEST, focusing on Political, Economic, Social and Technological aspects. Over time, the need to address Legal and Environmental factors led to the evolution of PEST into PESTLE analysis. This expansion reflects the growing complexity of the business environment, where legal compliance and sustainability have become crucial considerations. The incorporation of these additional factors allows organisations to build a more robust strategic plan. PESTLE analysis complements SWOT analysis, offering insights into external factors whilst SWOT examines both external and internal elements. This combined approach enhances decision-making by aligning organisational strengths with external opportunities while addressing potential threats.
Components of PESTLE analysis
Political factors
Government policies and stability
Government policies are a significant influence on business environments. Changes in taxation, labour laws, or trade restrictions can alter market dynamics. Political stability is equally important, as it fosters a predictable environment for investment. Businesses must monitor policy changes to maintain compliance and align strategies with governmental priorities.
Trade regulations and tariffs
Trade regulations and tariffs affect businesses entering or expanding in new markets. Import duties may limit market access whilst trade agreements can create opportunities. Understanding these regulations helps businesses navigate international markets effectively, mitigating risks associated with cross-border trade.
Economic factors
Economic growth and exchange rates
Economic growth is a key indicator of market potential. During periods of growth, consumer spending typically increases, leading to higher demand for goods and services. Exchange rates also play a pivotal role, affecting the cost of imports and exports. Businesses must adapt pricing and sourcing strategies to manage currency fluctuations.
Inflation and interest rates
Inflation and interest rates profoundly impact consumer behaviour. High inflation erodes purchasing power, while interest rates influence borrowing costs. Businesses must adjust their pricing strategies to remain competitive and manage debt effectively during fluctuating economic conditions.
Social factors
Cultural norms and demographics
Cultural norms and demographics shape consumer preferences and behaviours. Understanding these social factors helps businesses tailor products and marketing strategies to meet the needs of diverse populations. Demographic shifts, such as an ageing population, can also create new market opportunities.
Lifestyle changes
Lifestyle changes, driven by shifts in social values and technological advancements, affect consumer demands. As lifestyles evolve, businesses must innovate to offer products and services that align with emerging trends, such as increased health consciousness or digital engagement.
Technological factors
Technological advancements
Technological advancements drive business transformation by enhancing operational efficiency and enabling new business models. Companies must stay abreast of technological trends to capitalise on innovation, whether through automation, artificial intelligence, or other emerging technologies.
Research and development
Investment in research and development (R&D) is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Businesses that prioritise R&D can lead in innovation, delivering unique products and services. This focus on R&D supports long-term growth and adaptability in a rapidly changing market.
Legal factors
Employment and labour laws
Employment and labour laws affect human resources by governing hiring practices, workplace safety, and employee rights. Businesses must ensure compliance with these laws to avoid litigation and foster a fair and productive work environment.
Regulatory compliance
Regulatory compliance is vital for business operations across various sectors. Organisations must follow advertising standards, consumer protection legislation and product safety requirements. By doing so, they protect themselves from legal issues and build consumer trust, ensuring long-term success in the marketplace.
Environmental factors
Climate change and sustainability
Climate change and sustainability are increasingly important for industries worldwide. Businesses must consider their environmental impact and adopt sustainable practices to meet consumer expectations and regulatory requirements. This focus on sustainability can also result in cost savings and enhanced brand reputation.
Environmental regulations
Compliance with environmental regulations is essential for legal operation and maintaining a positive public image. Regulations may dictate waste management, emissions, and resource usage. Organisations must adapt processes to meet these standards, reducing their environmental footprint and avoiding legal penalties.
This framework provides businesses with a structured approach to analysing external factors, enabling informed strategic planning. By understanding these components, organisations can position themselves to navigate challenges and seize opportunities effectively.
Application of PESTLE analysis in strategic planning
Identifying opportunities and threats
PESTLE analysis is a vital tool for recognising external opportunities and threats. By systematically examining Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors, businesses can identify potential growth areas and foresee challenges. This analysis enables organisations to adapt their strategies, ensuring they remain competitive. For instance, a change in government policy might present a new market opportunity, while economic downturns could pose threats that need mitigation. Understanding these dynamics allows companies to capitalise on favourable conditions and devise contingency plans for adverse scenarios, thus enhancing their strategic positioning.
Integrating PESTLE with SWOT analysis
Integrating PESTLE with SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive strategic framework. While PESTLE focuses on external factors, SWOT examines internal strengths and weaknesses alongside external opportunities and threats. This combined approach offers a holistic view of the business environment, facilitating informed decision-making. By using PESTLE to inform SWOT, organisations can align their internal capabilities with external conditions, optimising strategic initiatives. This synergy not only aids in identifying areas for improvement but also highlights where the business can excel. Furthermore, the integration of these analyses can reduce stress and enhance confidence among stakeholders by providing clarity and direction. In workplace settings, this combined approach fosters a proactive culture, encouraging employees to anticipate changes and innovate accordingly. Ultimately, this strategic alignment drives sustainable growth and resilience in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Creating a PESTLE analysis template
Key elements to include
A comprehensive PESTLE analysis template should encompass all six macro-environmental factors: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental. For each factor, consider including:
- Political: Government policies, stability, tax policies
- Economic: Growth rates, inflation, exchange rates
- Social: Demographics, lifestyle changes, cultural norms
- Technological: Innovations, R&D trends, technological infrastructure
- Legal: Employment laws, regulatory compliance, industry-specific regulations
- Environmental: Climate policies, sustainability initiatives, environmental regulations.
These elements are crucial for gaining a holistic view of external influences on the organisation.
Steps to develop your template
Creating a tailored PESTLE template involves a step-by-step approach:
- Identify relevant factors: Begin by listing factors that are pertinent to your industry and geographical location.
- Research and gather data: Collect data from reliable sources to understand the impact of each factor.
- Organise information: Structure the data under the relevant categories in the template.
- Evaluate Impact: Assess how each factor might present opportunities or threats.
- Review and update: Regularly revisit the template to incorporate new developments.
By following these steps, you can ensure your PESTLE analysis remains relevant and actionable. This structured approach not only aids strategic planning but also reduces uncertainty, fostering a stable environment for decision-making. In turn, this can enhance workplace morale by clarifying organisational priorities and aligning them with external realities.
Real-world examples of PESTLE analysis
Case study 1: Industry application
In the automotive industry, PESTLE analysis has been instrumental in shaping strategic decisions. For instance, the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is influenced by several PESTLE factors. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter emissions regulations and offering subsidies to promote EV adoption. These political and environmental factors create opportunities for car manufacturers to innovate. Organisations that proactively adapt to these changes by investing in R&D and expanding their EV offerings can gain a competitive edge, aligning with both consumer demands and regulatory pressures.
Case study 2: Country analysis
PESTLE analysis is also valuable for assessing national economic conditions, as demonstrated in the case of India. The country presents diverse market opportunities and challenges, with varying economic conditions across different regions and sectors. However, challenges such as complex legal regulations and environmental concerns persist. By applying PESTLE, businesses can navigate India’s dynamic market landscape. Understanding these factors helps organisations tailor their strategies to leverage economic opportunities while addressing social and legal challenges, ultimately facilitating successful market entry and expansion. This approach reduces strategic uncertainty, leading to enhanced organisational confidence and stability.
Conclusion
PESTLE analysis is a crucial tool in strategic planning and decision-making. It provides a comprehensive view of external factors influencing an organisation, enabling businesses to identify opportunities and mitigate threats. By integrating PESTLE with other analytical tools, organisations can develop informed strategies that align with both internal strengths and external realities. This approach not only enhances operational effectiveness but also reduces strategic uncertainty. In workplace settings, the use of PESTLE instils confidence and clarity, contributing to stress reduction and improved decision-making. Ultimately, PESTLE analysis supports sustainable growth and competitive advantage in a complex business environment.
FAQs
What is the difference between PEST and PESTLE analysis?
PEST analysis stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors. PESTLE expands this framework by including Legal and Environmental factors. This expansion provides a more comprehensive view of external influences on a business.
How frequently should organisations conduct PESTLE analysis?
Organisations should review their PESTLE analysis quarterly to monitor changes in external factors and adjust strategies accordingly.
Can PESTLE analysis be used for small businesses?
Yes, PESTLE analysis is valuable for small businesses. It helps them understand the external environment, identify opportunities, and mitigate risks. This knowledge is crucial for strategic planning and competitive positioning.
What are the limitations of PESTLE analysis?
PESTLE analysis can be subjective, relying on the accuracy of available data and the analyst’s interpretation. It may not capture rapid changes, and its broad scope can make it challenging to focus on specific business needs.
How does PESTLE analysis contribute to risk management?
PESTLE analysis contributes to risk management by identifying external threats and opportunities. It informs strategic decisions and helps businesses prepare for potential challenges, reducing uncertainty and enhancing organisational resilience.
Infographic