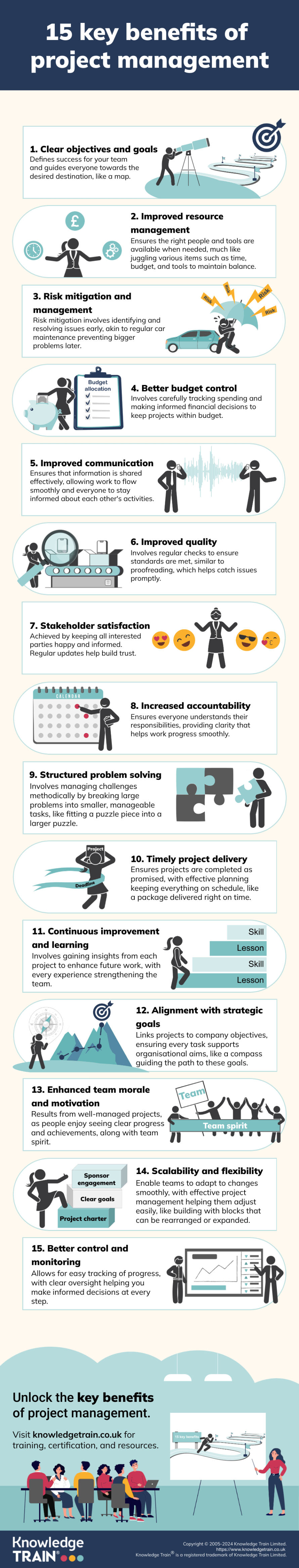
Project management benefits
Key takeaways
Strong project management improves delivery, governance, and organisational confidence.
- Clear roles, accountability, and stakeholder communication improve decision-making and reduce conflict.
- Structured planning and sequencing cut waste, optimise resources, and improve budget control.
- Regular monitoring and quality standards increase on-time delivery and reduce errors and rework.
- Better risk management and realistic estimating strengthen ROI and limit scope creep.
- Consistent methods, feedback loops, and lessons learned build morale, customer trust, and continuous improvement.
Introduction
Project management is a systematic approach to planning, executing, and completing work to achieve specific objectives. It involves coordination of resources, time, and personnel to ensure successful outcomes. Project management has become a crucial tool for organisations of all sizes.
Modern businesses face several challenges, such as increased competition, technology shifts, and diverse stakeholder expectations.
Project management provides a framework to enhance operations, mitigate risks, and improve efficiency.
By implementing effective project management practices, organisations can improve their ability to consistently deliver high-quality results. This allows businesses to respond to market changes and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
The core benefits of project management
Project management provides a range of benefits that can significantly enhance an organisation’s performance and results.
Improved decision-making and governance
Clear roles and responsibilities are the foundation of effective project management. It ensures team members know what to do, creates accountability, and prevents conflicts.
Stakeholder management is another crucial element of project management. By implementing a structured approach to communication, project managers can identify key stakeholders, address their concerns in advance, and align project goals with stakeholder expectations.
Enhanced efficiency and resource utilisation
Project management enables streamlined processes and workflows. It leads to reduced redundancies, improved task sequencing, and better utilisation of resources. Project management significantly improves resource allocation. It allows managers to assign personnel based on their skills and availability, better allocate budgets, and optimise use of equipment and materials.
Increased project success rates
One of the most tangible benefits is the ability to meet deadlines and stay within budget. Project management enables this by setting realistic timeframes, monitoring progress regularly, and taking corrective actions promptly.
Finally, project management enables delivery of high-quality results. It is achieved by establishing clear quality standards, implementing robust quality control measures, and continuously improving based on feedback and lessons learned.
By focusing on these core benefits, organisations can significantly improve their project results, leading to improved performance and competitiveness in their respective markets.
Tangible impacts on business performance
Implementing effective project management practices provides tangible benefits for organisations across various aspects of their operations.
Cost savings and financial benefits
Reduced waste and overruns are major benefits of project management. By implementing robust planning and control measures, organisations can avoid unnecessary expenditures, prevent scope creep, and identify potential cost overruns in advance.
Project management also leads to improved ROI on projects. It is achieved by better allocation of resources, more accurate cost estimates, and improved risk management strategies.
Time management and productivity gains
Faster project completion is one of the major benefits of effective project management. It is achieved by techniques such as critical path analysis and Agile methodologies. They allow identifying critical tasks, eliminating bottlenecks, and streamlining workflows.
Project management also enables better use of team members’ time. It is achieved by establishing clear roles and responsibilities, better task allocation based on skills and availability, and eliminating idle time between project phases.
Quality improvements and consistency
Standardised processes lead to better results. Project management frameworks provide clear quality standards and expectations, consistent methodologies across projects, and improved communication and collaboration.
Another tangible benefit is reduced errors and rework. It is achieved by implementing robust quality control measures, encouraging continuous feedback and improvement, and utilising lessons learned from previous projects.
By focusing on these tangible impacts, organisations can measure the value of project management and justify its implementation across various departments and initiatives. Improved cost management, time efficiency, and quality significantly contribute to business performance and competitiveness.
Intangible benefits and organisational culture
While tangible benefits are easy to measure, project management provides significant intangible benefits that enhance organisational culture and performance.
Enhanced team morale and collaboration
Clear communication and expectations are key elements of effective project management. It reduces misunderstandings and conflicts, creates a sense of purpose for team members, and fosters a collaborative work environment.
The structured approach of project management often leads to improved job satisfaction. Team members benefit from clear roles and responsibilities, opportunities for skill development, and recognition of individual and team achievements.
Improved customer satisfaction
Project management facilitates better alignment with customer needs by engaging stakeholders regularly, implementing iterative feedback loops, and being flexible to respond to changing requirements. Customers also appreciate predictable and reliable deliverables from consistent project management methodologies, transparent progress reporting, and proactive risk management.
Knowledge sharing and continuous improvement
Project management encourages capturing and sharing lessons learned and best practices. It prevents repeated mistakes, improves future project results, and enhances overall organisational efficiency.
Building project management capability is a long-term benefit that creates a culture of continuous improvement, develops a pool of skilled project managers, and enables the organisation to tackle more complex initiatives.
These intangible benefits significantly contribute to a positive organisational culture and long-term success, enabling a growth-oriented, collaborative, and excellent work environment.
Implementing project management
Successful implementation of project management requires careful planning and consideration of a few factors.
Choosing the right methodology
The choice of an appropriate project management methodology is crucial for project success. Traditional methodologies, such as Waterfall, provide a structured, linear progression through project phases. These methodologies work best in projects with clear requirements and limited changes.
On the other hand, Agile methodologies focus on flexibility and iterative development. They are more suitable for projects with evolving requirements or unknown outcomes.
Organisations should customise their chosen methodology to their specific needs. It involves analysis of project types, team dynamics, and organisational culture. A hybrid approach, combining elements of different methodologies, might be suitable for some organisations.

Agile method
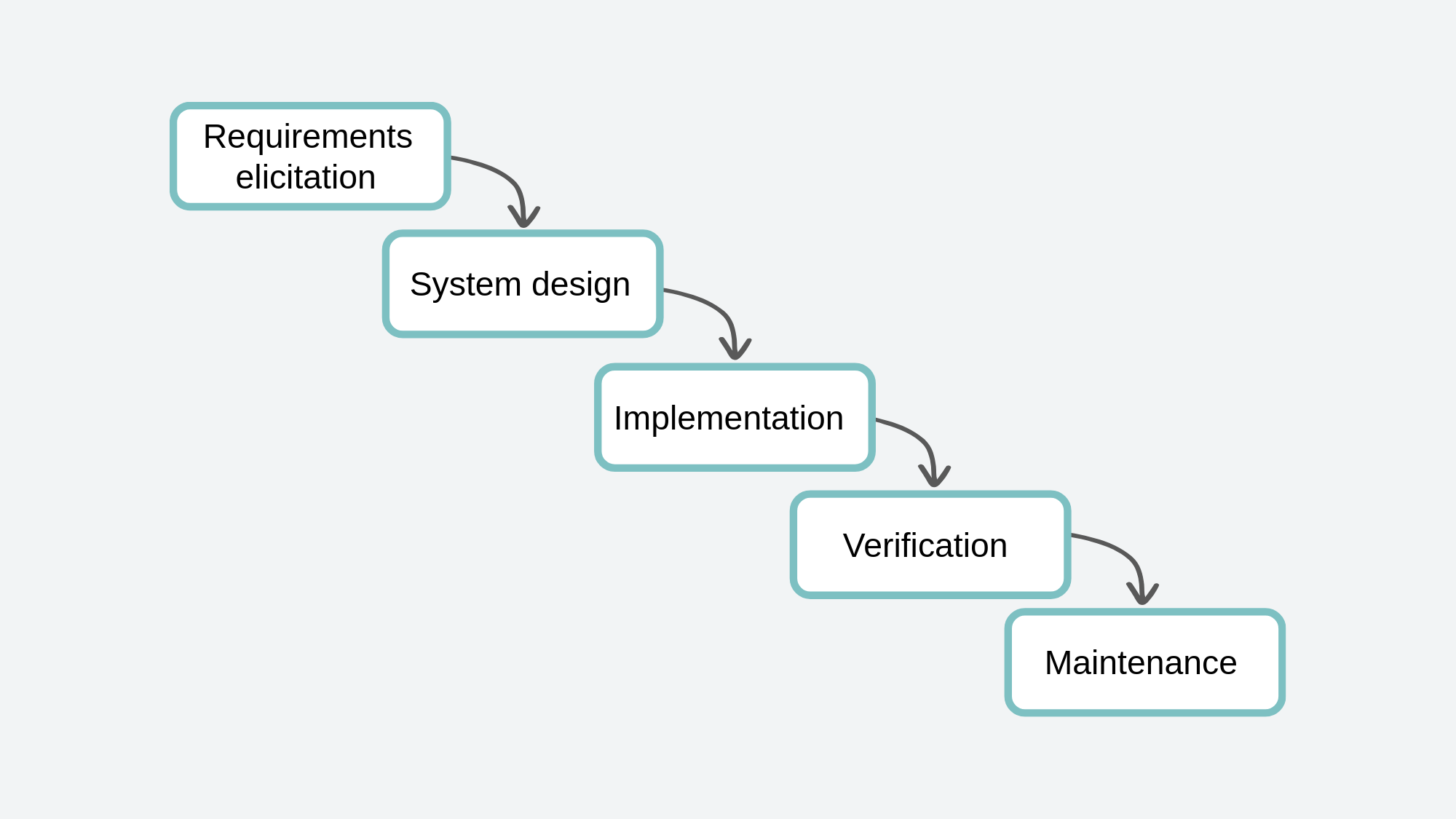
Waterfall method
Tools and technology
Selecting the right software is critical to successful implementation. Modern options offer features such as task tracking, resource management, and real-time collaboration. Key factors to consider include ease of use, scalability, and integration.
Integration with existing systems is vital for a smooth transition. Choose tools that can integrate with current enterprise software, such as CRM or ERP. This will ensure data flow and avoid double data entry.
Training and skill development
Certifications such as PMP (Project Management Professional) or PRINCE2 can significantly enhance team skills. They provide a strong foundation in project management principles and best practices.
However, certification alone is not enough. Organisations should create ongoing learning and development programmes. This could include internal workshops, mentoring programmes, and attendance at industry conferences. Continual development ensures that project management processes keep up with industry trends and organisational needs.
By considering these factors carefully, organisations can create a solid project management framework for success and growth.
Overcoming common challenges
There are many challenges that organisations face when implementing project management.
- One common challenge is resistance to change, as staff may be reluctant to adopt new methodologies. To overcome this, organisations should communicate the benefits of project management and involve staff in the implementation process.
- Another challenge is resource constraints. Limited budgets or staff may prevent organisations from adopting comprehensive tools or training programmes. Prioritising key components and implementing changes incrementally can help address this issue.
- Finally, finding the right balance between rigour and flexibility is critical for effective project management. Too much rigidity can stifle creativity and flexibility, while too little structure can lead to chaos. Organisations should aim for a middle ground, establishing core processes while allowing for adjustments based on the needs of each project.
By acknowledging and addressing these challenges, organisations can navigate the transition to effective project management practices and reap the associated benefits.
Conclusion
Project management offers numerous benefits to organisations, including improved decision-making, increased efficiency, and improved project success rates. These benefits translate into tangible impacts such as cost savings, productivity gains, and quality improvements. Less tangible benefits include enhanced morale and knowledge sharing, which contribute to a positive organisational culture.
While implementing project management practices may be challenging, the benefits far outweigh the initial hurdles. By carefully selecting methodologies, tools, and training programmes, organisations can customise their approach to suit their needs. We encourage businesses of all sizes to embrace project management principles, as they provide a strong framework for achieving strategic goals and long-term success.
FAQs
What is the difference between project management and general management?
Project management is focused on temporary projects with specific goals and deadlines. General management involves ongoing operations and broader organisational oversight. Project managers manage resources for specific goals, while general managers oversee daily business operations.
How can small businesses benefit from project management?
Small businesses can improve efficiency, save money, and enhance customer satisfaction through project management. It helps to prioritise tasks, manage resources effectively, and deliver products or services on time. Project management also supports growth by providing a structured approach to new initiatives.
What are the essential skills for effective project managers?
Key skills include communication, leadership, problem-solving, and time management. Technical knowledge, risk management skills, and adaptability are also important. Successful project managers are skilled at managing stakeholders and possess strong analytical and organisational skills.
How does project management contribute to risk mitigation?
Project management includes risk assessment and mitigation. It identifies potential risks early on, develops contingency plans, and monitors risks throughout the project life cycle. This approach reduces the impact of unforeseen events on project outcomes.
Can project management principles be applied to non-traditional industries?
Yes, project management principles can be applied to various industries. Industries such as healthcare, education, and creative fields can adapt project management methodologies to improve processes and outcomes.
What are the key metrics for measuring project management success?
Key metrics include on-time delivery, adherence to budget, scope fulfilment, and stakeholder satisfaction. Quality metrics, team productivity, and return on investment are also valuable measures of project management success.
How often should project management processes be reviewed and updated?
Processes should be reviewed regularly, typically annually or bi-annually. Organisations should also review processes after significant projects or changes in the market. Continual improvement ensures that project management processes are aligned with business goals and industry standards.
Infographic