Project management vs programme management
Dive into the differences between project and programme management to determine which is best suited for your organisation and can improve your project delivery. Read on to find out more.

Introduction
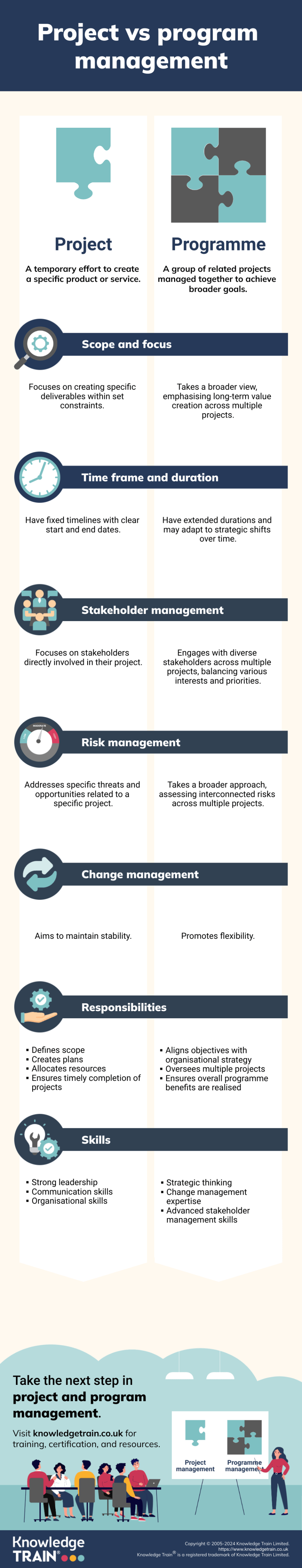
Project management and programme management are two distinct approaches to managing work within organisations. While both disciplines aim to deliver successful outcomes, they differ in scope, objectives, and methods.
Project management is a well-known practice that focuses on achieving specific outputs or deliverables within predefined constraints such as time, cost, and scope. On the other hand, programme management takes a broader perspective, coordinating and overseeing multiple related projects to realise strategic benefits for the organisation. Understanding the differences between project and programme management is crucial for effective resource allocation, stakeholder management, risk mitigation, and organisational agility.
By grasping the nuances of these two management approaches, organisations can better navigate the complexities of the modern business environment, improve their success rates, and drive sustainable growth.
Understanding projects and programmes
What is a project?
A project is a temporary endeavour undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result. It is a fundamental unit of work within organisations, often characterised by a specific purpose and an end goal.
Characteristics of projects
- Defined scope: Projects have clear boundaries and deliverables
- Temporary nature: Projects have fixed start and end dates
- Unique output: The end product or result is distinct from routine operations
- Resource constraints: Projects are typically limited by budget, time, and personnel.
Project objectives and constraints
Projects are designed to achieve specific objectives or goals within certain constraints. The triple constraint model is a common framework that identifies three key factors:
- Time: Projects must adhere to deadlines and milestones
- Cost: Projects must stay within budget allocations
- Scope: Projects must deliver agreed-upon features and functions.
Project managers must balance these constraints to ensure successful project delivery.
What is a programme?
A programme is a group of related projects that are managed in a coordinated manner to achieve benefits that would not be available if the projects were managed individually.
Characteristics of programmes
- Multiple projects: Programmes involve the coordinated management of several interrelated projects
- Longer duration: Programmes typically last several years or may be ongoing
- Strategic focus: Programmes are aligned with the organisation’s goals
- Evolving nature: Programmes adapt to changing business needs.
Programme objectives and strategic alignment
Programmes focus on realising strategic benefits for the organisation. They are concerned with creating value and supporting business objectives. Key aspects of programmes include:
- Value creation: Delivering outcomes that contribute to the organisation’s strategic goals
- Change management: Facilitating organisational transformations and initiatives
- Stakeholder engagement: Managing complex relationships across multiple projects
- Risk mitigation: Addressing broader and long-term risks.
Programme managers are responsible for ensuring that individual projects within the programme contribute to the overall strategic objectives. They maintain flexibility to adapt to changing business environments while maximising benefits realisation.
In conclusion, understanding the distinctions between projects and programmes is critical for effective management and organisational success. By recognising the differences in scope, objectives, and management approaches, organisations can better allocate resources, manage stakeholders, and navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape.
Key differences between project and programme management
It is of crucial importance for the representatives of organisational leadership to have a good awareness of key difference between project and programme management, which will be further elaborated by focusing on five areas.
Scope and focus
Project management
Project management is defined by the creation of specific deliverables within a defined scope and set of constraints. The emphasis is placed on achieving measurable objectives, completing tasks efficiently, and producing tangible results.
Project managers are focused on delivering according to predetermined quality standards while optimising resource use.
Programme management
Programme management, on the other hand, has a wider perspective and is oriented towards long-term value creation. Aspects such as aligning multiple projects with organisational strategy, maximising benefits across interrelated initiatives, and adapting to changing business needs are central to programme management.
Programme managers focus on the overall outcomes and results that align with strategic objectives.
Time frame and duration
Projects
Projects are time-bound activities. They typically have fixed start and end dates and a defined project lifecycle. Milestones and deadlines are established to track progress, and projects are often closed once the deliverables are completed.
Project managers are primarily concerned with adhering to the schedule and delivering on time.
Programmes
Programmes, in contrast, can span longer timeframes. They often have more fluid timelines that can adapt to shifts in strategy and priorities. Evaluation and adjustment are ongoing processes, and programmes may continue for as long as they are delivering benefits.
Programme managers have a long-term perspective and balance short-term project requirements with future opportunities.
Stakeholder management
Project level
Project stakeholder management is a targeted approach that focuses on individuals or groups directly impacted by the project. This includes managing expectations within the project’s scope and ensuring communication of project-specific information.
Project managers build and maintain relationships critical to the project’s immediate success.
Programme level
Programme stakeholder management is a broader approach that involves engaging a wider range of stakeholders across multiple projects within a programme. Balancing the conflicting interests and priorities of these stakeholders and fostering long-term relationships beyond the lifecycle of individual projects is a key aspect of programme stakeholder management.
Programme managers navigate complex stakeholder networks to maintain support for the programme.
Risk management
Project risks
Project risk management centres on specific risks and opportunities associated with a project. This includes identifying risks within the project’s scope, developing risk response strategies for known risks, and continuously monitoring and controlling risk impacts on project objectives.
Project managers aim to minimise uncertainty and potential threats to project outcomes.
Programme risks
Programme risk management takes a broader perspective and considers the interconnected risks across multiple projects. This involves managing strategic risks that can impact organisational goals and adapting to emerging risks and opportunities that arise during the programme’s lifecycle.
Programme managers have a holistic view of risk and consider its implications on the entire programme.
Change management
Projects
Change management within projects is often focused on minimising disruptions and changes to the project’s scope and plan. The goal is to maintain stability and adhere to the defined project constraints and objectives.
Project managers often implement strict change control procedures to prevent scope creep and stay on track.
Programmes
Change management within programmes, on the other hand, is more adaptive and flexible. Programmes embrace change as an opportunity for improvement and benefit maximisation. Programme managers may encourage adaptive responses to shifting priorities, realign projects to capitalise on new opportunities, and continuously optimise the programme’s outcomes.
Programme managers leverage change to drive value creation across the programme.
Understanding these core differences allows organisations to take full advantage of both project and programme management.
Roles and responsibilities
Project and programme managers play pivotal roles in the success of organisational initiatives. This section provides an overview of their key responsibilities, the essential skills they should possess, and the dynamics of their collaboration for optimal results.
Project manager
| Key responsibilities | Skills and competencies |
| Defining project scope and objectives | Strong leadership and team management |
| Creating and managing project plans | Excellent communication and negotiation abilities |
| Allocating resources effectively | Analytical and problem-solving capabilities |
| Monitoring progress and ensuring timely completion | Time management and organisational proficiency |
| Managing project risks and issues | Technical knowledge relevant to the project domain. |
| Communicating with stakeholders. |
Programme manager
| Key responsibilities | Skills and competencies |
| Aligning programme objectives with organisational strategy | Vision and strategic thinking |
| Overseeing multiple project managers and their projects | Change management expertise |
| Managing interdependencies between projects | Advanced stakeholder management skills |
| Ensuring overall programme benefits realisation | Financial acumen and budget oversight |
| Adapting the programme to changing business needs | Risk management across multiple projects |
| Engaging with senior stakeholders and executives. | Leadership in complex, ambiguous environments. |
How project and programme managers work together
Project and programme managers collaborate in various ways to drive organisational success. Key aspects of their interaction include:
- Clear communication: Both roles exchange regular updates and information.
- Aligned objectives: Project goals support and align with the programme’s desired outcomes.
- Resource optimisation: They coordinate resource allocation across projects for efficiency.
- Risk mitigation: Potential cross-project risks are identified and addressed collaboratively.
- Change management: Adaptations are made to changes in programme strategy.
- Stakeholder engagement: Communication at different levels is coordinated.
Working in unison, project and programme managers create synergy that elevates the organisation’s overall performance.
Tools and methodologies
Project and programme management often require specialised tools and methodologies to succeed. This section highlights some of the most prominent tools and techniques used in both fields, including approaches like Agile and DevOps.
Project management tools and techniques
Project managers have a wide array of tools and techniques to guide them through the stages of project management. These include:
- Gantt charts: A visual way to schedule and track project tasks over time.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): A hierarchical decomposition of the project’s deliverables.
- Critical Path Method (CPM): A technique for identifying the most important project activities.
- Resource levelling: A method for optimising the allocation of resources across different project tasks.
- Earned Value Management (EVM): A process for measuring project performance and progress.
- Risk registers: A document that lists potential project risks and their impacts.
Microsoft Project, Asana, and Trello are examples of software commonly used for project management.
Programme management tools and techniques
Programme managers use a different set of tools that allow them to oversee multiple projects and align them with the strategic goals. Some of the techniques include:
- Portfolio management software: Software to help manage multiple projects and programmes.
- Benefits realisation tracking: Tracking and measuring the outcomes of a programme.
- Dependency mapping: Mapping the relationships between different projects and initiatives.
- Stakeholder analysis matrices: Identifying and prioritising key stakeholders.
- Programme roadmaps: Long-term planning and strategy documents.
- Resource capacity planning: Optimising the allocation of resources across different programmes.
Tools like Jira Align and Planview are commonly used in programme management.
Agile and DevOps in programme management
Agile and DevOps are methodologies that can also be applied to programme management to promote flexibility and collaboration.
- Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe): A framework for applying Agile practices at the programme level.
- Kanban boards: A visual tool for tracking the flow of work and identifying bottlenecks.
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): An approach to automating the software delivery process.
- Feature-driven development: A process for developing software features that align with business value.
- Programme increment planning: Coordinating multiple Agile teams within a programme.
These tools and methodologies empower project and programme managers to thrive in complex and dynamic environments, ensuring successful outcomes.
Benefits of effective programme management
Effective programme management can provide significant benefits to organisations. Here are four benefits that can contribute to the overall success of a business:
Improved strategic alignment
When programmes are well-managed, it can help ensure that projects and initiatives are aligned with organisational goals. This can lead to improved focus on long-term objectives, better prioritisation of projects and resources, and a greater likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
Programme managers take a holistic view to ensure that individual projects are contributing towards common strategic targets.
Better resource management
Programme management can also help optimise the use of resources across multiple projects. This can include personnel, budget, and equipment. When managed effectively, resources are used more efficiently and effectively across the board.
Programme management also helps to reduce the potential for conflicts between projects for resources and better aligns capacity planning and utilisation.
Enhanced stakeholder engagement
Effective programme management also allows for enhanced stakeholder relationships. This is because stakeholders see a consistent approach to communications across all projects.
Programme management helps to keep all stakeholders informed of the benefits they can expect to see from the delivery of the projects that make up a programme. This increased visibility of expected benefits can lead to increased stakeholder buy-in and support.
Increased organisational agility
By taking an effective programme management approach, an organisation can also become more agile. In other words, they can be able to respond more quickly to changes and adapt more effectively.
Programme management also helps with enabling quicker decision-making, as an organisation can gain valuable insights from taking a programme view to achieve its strategy.
In conclusion, effective programme management can lead to a range of benefits for organisations. These include improved strategic alignment, better resource management, enhanced stakeholder engagement, and increased organisational agility.
Challenges in programme management
In the world of programme management, there are a variety of challenges that programme managers face. It is important to understand the most common challenges to have the best chance at overcoming them. Here are the top four challenges to be aware of.
Balancing multiple projects and priorities
In any given programme, it is important to keep track of and prioritise multiple projects. This means that resources must be allocated appropriately across projects, different project timelines and milestones must be managed, and project objectives need to be met.
Managing complexity and uncertainty
Programme managers often have to manage a variety of different, complex projects. These can include projects with interdependencies and business environments that are constantly changing. As a result, there are risks involved with each project that must be mitigated.
Ensuring effective communication across projects
To ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page and have a clear understanding of the project, it is important to have effective communication at all levels. This can be done by establishing an information flow between stakeholders, aligning messages across projects, and avoiding information silos or miscommunication.
The most effective way to ensure communication is to have an established programme manager role who has the skills, tools, and processes in place to manage all communication effectively.
Acknowledging and addressing these challenges empowers programme managers to effectively steer their teams towards success and create value for their organisations.
Best practices for successful programme management
Ensuring the success of programme management requires the adoption of proven strategies and methodologies. In this section, we will discuss 4 best practices for successful programme management.
Establishing clear programme governance
Setting up a strong programme governance framework is crucial for effective programme management. This involves establishing clear roles and responsibilities for all programme stakeholders, developing a decision-making framework to address programme-level issues, and creating escalation paths to handle conflicts and create programme-specific policies and procedures.
A well-defined governance structure provides clarity and accountability throughout the programme lifecycle.
Developing a robust benefits realisation plan
To effectively track and deliver programme value, it is important to have a robust benefits realisation plan in place:
- Identify and quantify the expected benefits of the programme
- Map the benefits to specific projects and deliverables
- Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the programme
- Establish a timeline for the realisation and measurement of the programme benefits.
This approach ensures that programmes are aligned with delivering tangible value to the organisation.
Fostering collaboration between project and programme teams
Effective teamwork is essential for programme success. This can be achieved by encouraging open communication channels between project and programme teams, facilitating regular cross-project meetings and knowledge-sharing sessions, implementing collaborative tools and platforms for seamless information exchange, and recognising and rewarding cross-team collaboration and problem-solving.
Strong collaboration and communication help enhance overall programme performance and minimise conflicts.
Implementing effective reporting and monitoring systems
Robust reporting and monitoring mechanisms are vital for effective programme oversight. This involves, developing standardised reporting templates to ensure consistent and structured information collection, implementing real-time dashboards to track programme progress and key performance indicators, setting up regular review cycles to assess programme health and alignment, and utilising data analytics to identify trends and potential issues in a timely manner.
With these systems in place, organisations can make informed decisions and manage their programmes proactively.
Organisations can benefit greatly by adopting these best practices to enhance their programme management and achieve success.
Conclusion
A clear distinction between project and programme management is essential for achieving success in organisational objectives. While project management primarily focuses on the efficient delivery of specific outputs within constraints, programme management takes a more strategic approach towards realising benefits across multiple initiatives. The key differences between the two methodologies can be seen in scope and focus, time frame and duration, Stakeholder and risk management approaches, and change management strategies.
Aligning both project and programme management approaches can result in enhanced achievement of strategic goals for organisations. Optimised resource allocation can be achieved, along with improved stakeholder engagement and increased adaptability to market changes.
By leveraging the strengths of both methodologies, organisations can effectively navigate complexities and drive sustainable growth in their respective industries.
FAQs
What is the main difference between a project and a programme?
A project focuses on the delivery of a specific output. In contrast, a programme coordinates multiple related projects to achieve broader strategic benefits.
Can a project manager transition into a programme manager role?
Yes, project managers can transition into programme manager roles but should acquire additional skills in strategic thinking, stakeholder management, and overseeing multiple interconnected initiatives.
How do you measure the success of a programme?
Programme success is measured through benefits realisation, strategic alignment, and long-term value creation for the organisation.
What are some common programme management methodologies?
Common programme management methodologies include MSP (Managing Successful Programmes), PgMP (Programme Management Professional), and Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe).
How does programme management support organisational strategy?
Programme management supports organisational strategy by aligning multiple projects with strategic objectives, ensuring efficient resource allocation, and driving long-term value creation.