Introduction
In PRINCE2 project management, exception management stands as a fundamental component. In PRINCE2 exception management teams identify deviations from project parameters then assess and address these issues. This process is fundamental to PRINCE2 because it helps project managers maintain control and achieve their project goals.
PRINCE2 uses exception management as a fundamental tool to achieve several benefits which together sustain project success.
- Optimise senior management time usage
- Encourage proactive problem-solving
- Improve project governance.
This article will cover:
- The ‘manage by exception’ principle
- Implementation approaches
- Seven performance aspects
- PRINCE2’s exception management technique
- Forecasting methods
- Effective practices.
Project managers who understand exception management become better equipped to tackle obstacles and maintain project trajectories. Professionals who want to thrive in PRINCE2 project settings should possess this knowledge to achieve ongoing successful outcomes.
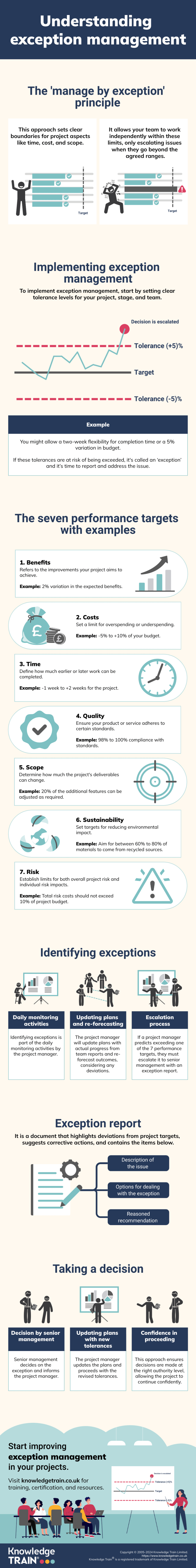
The ‘manage by exception’ principle
Understanding Management by exception
The PRINCE2 framework’s core principle ‘Manage by exception’ targets efficient project management. The system sets predetermined boundaries for project objectives which permits authority delegation as long as actions stay within those boundaries. Project managers can independently control daily operations while escalating any issues that surpass established tolerances.
Advantages of this principle include:
- Efficient use of senior management time
- Clear accountability at each project level
- Timely decision-making and problem-solving.
Tolerances in PRINCE2
Tolerances represent acceptable ranges of deviation from target goals which do not need higher management review. The implementation of “Manage by Exception” depends on the existence of tolerances.
Within PRINCE2 there are seven performance aspects that necessitate defined tolerances.
- Time
- Cost
- Quality
- Scope
- Risk
- Benefits
- Sustainability.
The tolerance levels apply to project management, stage management and team operations. The system enables project teams to track advancement while spotting potential problems before they escalate. Tolerances establish definitive boundaries which maintain project control but still permit flexible execution methods. Management attention remains concentrated on areas which results in improved project efficiency.
Implementing exception management
Establishing tolerances
The starting point for successful exception management lies in establishing precise tolerance parameters. These are established at three distinct levels:
- Project level: set by corporate or programme management
- Stage level: defined by the project board
- Team level: determined by the project manager.
Different aspects illustrate tolerance settings through examples such as time and cost deviations.
- Time: ±2 weeks for project completion
- Cost: ±5% of the agreed budget
- Quality: 98-100% compliance with specifications
- Scope: The scope requires full delivery of essential features while allowing flexibility for optional features.
Delegation of authority
Management levels operate efficiently through delegation when tolerances outline their operational boundaries. This approach allows:
- Project managers should make decisions while staying within the approved stage tolerances
- Team managers should keep work package deviations within predetermined boundaries.
The project board maintains overall control but steps in solely when tolerances are surpassed. This structure promotes autonomy while maintaining oversight.
Exception reporting process
Exception reporting becomes active when a tolerance breach is anticipated or takes place. The process typically follows these steps:
- Identification of potential or actual tolerance breach
- The project manager creates an Exception Report to address project deviations
- Submission to the project board for review
- Decision-making on corrective actions or project redirection.
Timely communication is crucial in exception reporting. The system allows teams to respond quickly to problems while reducing negative effects on project outcomes. Through consistent progress evaluations and check-ins teams can detect emerging exceptions early which enables them to manage proactively.
The application of these practices enables project teams to control exceptions which keeps projects aligned with their goals and parameters.
The seven aspects of performance in exception management
Effective exception management in PRINCE2 involves setting tolerances across seven critical performance domains. Project teams need to understand these performance aspects to maintain control over their projects and ensure they achieve successful results.
1. Benefits
The benefits aspect examines the tangible improvements produced through project execution. Benefit tolerances provide flexibility for both minor under-delivery and minor over-delivery.
Example: Increased income generation in a sales improvement project can vary by plus or minus 2%.
2. Costs
Cost tolerances define the allowed budget deviations which can be either higher or lower than the agreed budget amount.
Example: The project budget may fluctuate by ±5%.
3. Time
The allowable deviation from planned completion dates is specified by time tolerances.
Example: The stage end date may vary by up to two weeks from its scheduled completion time.
4. Quality
Quality tolerances establish the permitted deviation from the accepted criteria that were agreed upon.
Example: Software projects can achieve between 98% and 100% compliance with the specified functionality.
5. Scope
Scope tolerances define the allowable variation limits for project deliverables.
Example: A project must deliver all essential features while permitting optional features to be implemented with 20% flexibility.
6. Sustainability
This aspect measures the acceptable deviation between project activities or outcomes and sustainability targets.
Example: The construction project permits carbon emission targets to vary within a ±5% range.
7. Risk
Risk tolerances establish boundaries for total project risk and individual risk outcomes.
Example: Threat costs must remain under 10% of the budget collectively while ensuring each individual threat doesn’t surpass 5%.
Project managers who define precise tolerances for these seven elements can:
- Establish clear boundaries for decision-making
- Identify potential issues early
- Ensure appropriate escalation of exceptions
- Maintain a balance between flexibility and control.
Successful project outcomes result from effective performance management which enables decision-makers to respond appropriately and quickly to necessary changes.
Exception management technique in PRINCE2
Six-step exception management process
PRINCE2 manages exceptions through a structured approach that involves six distinct steps.
- Forecast: The team manager expects to exceed the allotted tolerance levels for a work package.
- Raise issue: The project manager receives an issue registration notice within the issue register.
- Escalate: When an issue impacts stage tolerances the project manager proceeds to draft an exception report.
- Review options: The project board assesses both the exception report and possible solutions.
- Create exception plan: The project manager creates a detailed plan to manage the exception when it becomes necessary.
- Implement: Once approved, the exception plan functions as the new stage plan.
Roles and responsibilities:
- Team manager: Forecasts exceptions and raises issues
- Project manager: Assesses issues, creates exception reports and plans
- Project board: The project board evaluates exception reports to determine necessary corrective measures.
Exception plans
Exception plans function as guides for managing substantial deviations outside accepted tolerance limits. Their primary purposes are to:
- The project manager develops a detailed plan outlining specific actions needed to correct the project’s path within acceptable tolerances
- Provide a revised baseline for project performance.
Creation process:
- Analyse the exception’s impact on the project
- Develop alternative courses of action
- Select the most appropriate solution
- Detail the implementation approach.
The exception plan takes over from the original stage plan to set the new standard for project execution and performance tracking after approval. The methodology enables projects to remain flexible to change while preserving defined goals and management controls.
PRINCE2 projects that utilise this structured process can manage exceptions efficiently by reducing their effects and preserving project progress.
Forecasting in exception management
Importance of forecasting
Forecasting serves as a key element in exception management because it facilitates early detection of potential issues. It allows project teams to:
- Anticipate deviations from tolerances
- Implement preventive measures early
- Develop strategies that reduce the potential negative consequences exceptions can create on project results.
Effective forecasting depends on multiple types of data sources.
- Historical project performance
- Current project metrics
- External factors affecting the project
- Risk assessments and probability analyses.
Tools and techniques for forecasting
Modern PRINCE2 forecasting approaches use sophisticated technology solutions and methods that emphasise data interpretation.
- Digital management systems:
- Integrated project management software
- Real-time data collection and analysis tools.
- Predictive analytics:
- Machine learning algorithms for trend identification
- Scenario modelling for risk assessment.
- Data trusts:
- Shared data repositories for benchmarking
- Industry-specific performance metrics.
Project management tools support managers in performing ‘what-if’ analyses to improve their decision-making processes. Teams can produce precise forecasts by merging historical data with current project details and predictive models. The method enables prompt detection of exceptions while managing project tolerances effectively.
Effective practices for exception management
Robust exception management implementation depends on following multiple essential practices.
Clear communication channels
Transparent communication pathways form the foundation of effective exception management.
- Define clear escalation procedures
- Ensure all team members understand reporting lines
- Utilise project management software for real-time updates
- Conduct regular team briefings on tolerance status.
Regular monitoring and reporting
Consistent oversight of project performance is crucial:
- Implement automated tracking systems for key metrics
- Conduct weekly reviews of tolerance levels
- Generate standardised reports for easy comparison
- Use visual dashboards to highlight potential exceptions.
Continuous learning and improvement
Enhancing exception management processes over time:
- Record detailed lessons in a log throughout the duration of the project
- Conduct post-exception reviews to identify improvement areas
- Distribute organisational insights to prevent similar problems from happening again
- Ensure that exception management procedures are consistently updated with new insights and learnings.
Project teams will achieve better exception identification and management through the integration of these practices while also learning from these exceptional events. Through this method organisations develop proactive management practices and ongoing improvement which results in better project results and stronger organisational skills in managing exceptions.
Conclusion
Effective project governance in PRINCE2 fundamentally relies on exception management. Project teams that apply the ‘manage by exception’ principle and establish explicit tolerances through structured processes can:
- Identify and address issues promptly
- Optimise resource allocation
- Maintain project control while allowing flexibility.
The seven performance aspects establish a complete system for overseeing the health of projects. When integrated with strong forecasting methods together with effective management practices exception management produces better project results.
Exception management expertise allows project managers to deal with obstacles in an effective manner. Through exception management projects stay aligned with their goals while adapting to changes and consistently delivering value. Project success over extended periods in complex settings requires mastery of this essential skill.
FAQs
What is the main goal of exception management in PRINCE2?
The main objective of the approach is to keep the project under control through quick detection and resolution of tolerance deviations.
How does ‘manage by exception’ compare to other project management approaches?
This approach delegates authority within defined boundaries which minimises micromanagement while boosting efficiency against conventional hierarchical management methods.
What are the seven aspects of performance in PRINCE2 exception management?
The seven aspects are: PRINCE2 exception management encompasses seven performance aspects which include time, cost, quality, scope, risk, benefits, and sustainability.
How often should teams review tolerances during a project?
Teams need to evaluate tolerances during stage transitions and through ongoing project progress reviews.
What is the project board’s role in exception management?
The project board establishes project-level tolerances, examines exception reports and decides on corrective actions whenever tolerances surpass allowable limits.
How does exception management help use senior management time efficiently?
Senior management can optimise their time allocation by intervening only when major issues occur since they delegate authority within established tolerances.
What is an exception plan, and when do teams create one?
An exception plan serves as a comprehensive approach for resolving tolerance breaches. Teams generate exception plans when predictions indicate that a stage will surpass its established tolerances.
How does forecasting contribute to effective exception management?
Through forecasting teams can detect potential tolerance breaches ahead of time to take early preventive actions and protect project results.
Infographic